TABLE 2.
Parameters for E. coli used in Figs. 2–4 and variables used in the model
| Parameter (i = 1,2) | Description | Value used | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| kSi | Maximum rate of synthetase i | 100 s−1 | (Pedersen et al., 1978) |
| kR | kcat of translation | 20 s−1 | (Bremer and Dennis, 1987) |
| kai | See Appendix A | 106 M−1s−1 | (Schomburg et al., 2002) |
| KSi | Dissociation constant of deacylated tRNA i and synthetase i | 10−6 M | (Schomburg et al., 2002) |
| Ki | Feedback inhibition constant for aai | 10−4 M | (Chassagnole et al., 2001b; Neidhardt et al., 1996) |
| KRi | Km for ternary complex i in protein synthesis | 10−6 M | (Pavlov and Ehrenberg, 1996) |
| t0i | Total concentration of tRNA for amino acid i | 10−5 M | (Dong et al., 1996) |
| [Si] | Total concentration of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase i | 10−6 M | (Pedersen et al., 1978) |
| r | Ribosome concentration | 1.67 × 10−5 M | (Bremer and Dennis, 1987; Donachie and Robinson, 1987) |
| fi | Usage frequency of amino acid i in protein synthesis | 0.05 | (Dong et al., 1996) |
| Variables |
Description |
||
| xi | Concentration of free amino acid i | ||
| yi | Concentration of ternary complex i | ||
| ti | Concentration of deacylated tRNA i | ||
| ki | Uninhibited amino acid i synthesis rate | ||
| si | Normalized uninhibited synthesis rate of amino acid i | ||
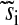 |
Normalized inhibited synthesis rate of amino acid i | ||
| JR | Total flow of amino acid into proteins | ||
| Jmax | Maximal flow of amino acid into proteins | ||
| v | Average translation rate per ribosome | ||
| vmax | Maximal translation rate per ribosome | ||
| γ | Fraction of RelA bound to the ribosome |
We estimate the experimental values to be correct with sufficient accuracy to allow for the analytical approximations in Table 1.
