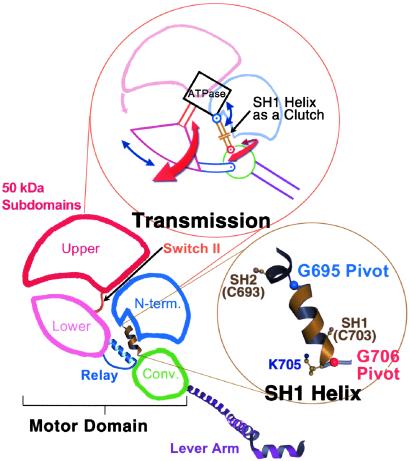
Figure 5.
Mechanical components of the motor. Schematic diagram of the myosin head (shown here in the near-rigor conformation), depicting the four subdomains of the motor together with the lever arm (light chains not shown). (Upper Inset) a mechanical representation of the motor's “transmission,” illustrated to highlight the roles of various components. Switch II functions like a piston by delivering work from the enzyme (“ATPase”) to the 50-kDa lower subdomain, which converts this work to rotational motion, roughly comparable to the role of a crank shaft. During the transition from the near-rigor to the pre-power stroke conformation (with the lever arm moving from “down” to “up”), the rotation of the 50-kDa lower subdomain can be divided into two roughly perpendicular vector components (red and blue arrows). The red arrows represent rotation about axes in the plane of the paper, and the blue arrows represent rotation about axes perpendicular to the plane of the paper (described previously as twist and tilt motions, respectively; ref. 40). The converter rotates about the glycine pivots along these vector components as shown (1, 10) and, in addition moves about a hinge in the relay (not shown, see text and ref. 1). During this transition, the molecule passes through the internally uncoupled state, in which the SH1 helix unwinds. The converter/lever arm orientation then becomes less constrained, and torque cannot be delivered from switch II to the converter/lever arm module. Thus, the function of the SH1 helix can be compared with that of an automobile clutch, which can disengage the gear train and drive shaft from the motor. Based on EM studies of myosin cross-bridges bound to actin and the x-ray crystallographic nucleotide-free near-rigor structure, it appears that rotation of the 50-kDa upper subdomain (pink arrow) on strong binding to actin closes the front of the cleft and triggers both the power stroke and product release (see text). A related two-dimensional mechanical model of the myosin motor has been published (41), but revisions are needed to agree with recent experimental findings. (Lower Inset) The SH1 helix flanked by the glycine pivots.