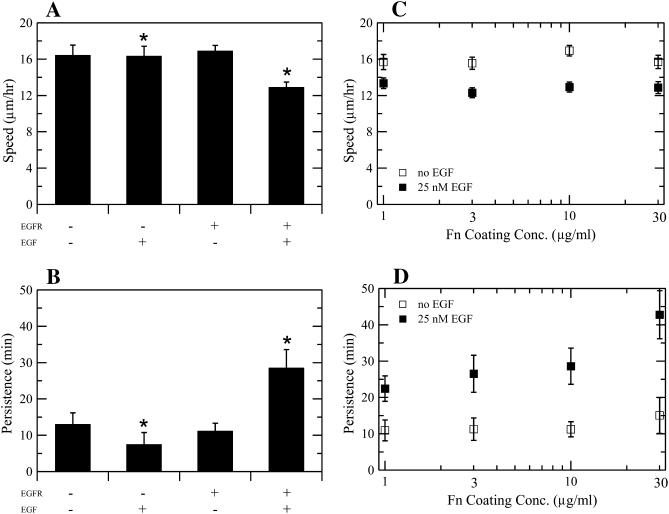
FIGURE 2.
Effects of EGF and Fn on speed and persistence for migrating CHO-EGFR cells. Transfection of EGFR-GFP into CHO K1 cells alters cell speed (A) and persistence (B) in the presence, but not the absence, of EGF. Data in A and B were obtained using a 10 μg/ml Fn coating concentration. Asterisks denote inequality at 95% confidence for key comparison. (C) EGF stimulation, but not Fn coating concentration, modulates CHO-EGFR speed. Single-factor ANOVA: p = 0.54 (S, −EGF), p = 0.90 (S, +EGF). (D) Persistence time increases with Fn coating concentration in the presence of EGF. ANOVA: p = 0.88 (P, −EGF), p = 0.03 (P, +EGF). To derive the speed of a single cell, total cell path length was divided by the total time of observation. Single cell persistence times were derived from nonlinear least-squares regression using individual cell speed and root mean-square displacement data as inputs. Reported S and P data represent the mean ± 2 SE for three experiments per condition, with 80–100 cells per experiment.