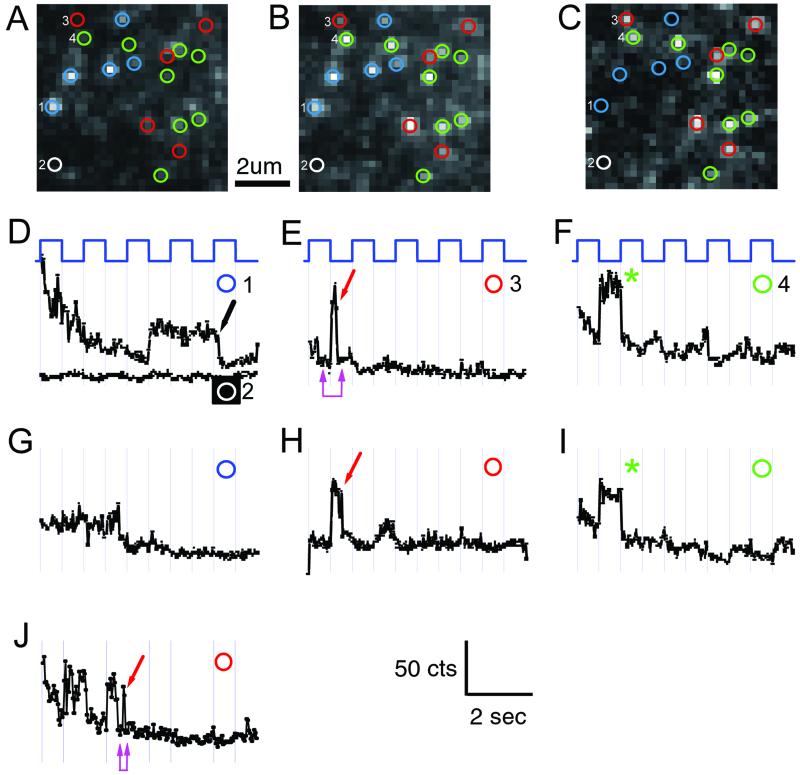
Figure 4.
Elementary ΔF of single TMRM molecules attached to 359C. (A–C) Voltage dependence of fluorescence detected on a 30 × 30 pixel region (6.75 × 6.75 μm on the cell surface; 1/16 of total CCD image). (A) Average of two frames at +20 mV, immediately before repolarization. (B) Average of two frames immediately after repolarization from +20 to −100 mV. (C) Spots where intensity was modulated by voltage were all brighter at negative voltage, characteristic of 359-TMRM channels, and were identified for analysis as bright spots in the difference image (C = B − A). (D–J) Trajectories of fluorescence intensity of four spots (D–H from optical patch in A–C and J from another patch) (y axis range = 270–450 counts) during a 10-s movie. Abrupt irreversible decreases in fluorescence are quantal bleach events (arrows). Elimination by quantal bleaching of further response to voltage identifies single-channel trajectories (red arrows). (D and G) Bright spots that did not respond to voltage (blue circles) are likely TMRMs attached to nonchannel proteins; nonresponsive dim spots (white circles) are background. (E, F, and H–J) 359-TMRM spots bleached in either the bright state (red circles and arrows), or did not get bright again upon repolarization, indicating bleaching in the preceding dim state (green circles and asterisks). (Numbers in D–F correspond to pixels numbered in images A–C.) (E, F, and I) The dim state is strongly quenched and indistinguishable from the background after bleaching: (i) No difference between dim-state intensity at +20 mV before bleaching and background at −100 mV after bleaching (E and J double magenta arrow); (ii) dim-state bleaching (in F and I) (green asterisk) occurs without measurable decrease in fluorescence. Note that small voltage-driven ΔF remaining after bleach (F and H) is likely from channels farther from the coverslip. High-intensity illumination: 1.2 mW per 20-μm-diameter spot. Steps are from holding potential of −100 mV in 50% duty cycle between −100 mV and +20 mV (1 s at each voltage). (20 frames per s.)