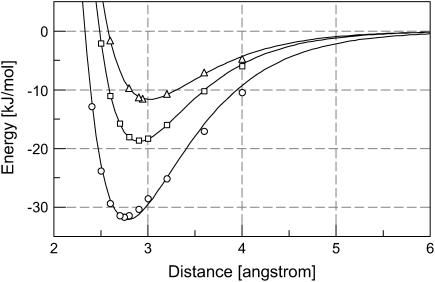
FIGURE 2.
Hydrogen-bond dissociation energy of a protonated carboxylic group (butyric acid) interacting with a methanol molecule. The hydrogen-bond dissociation energies were calculated at selected bond lengths using B3LYP/6-311+G(2d,p) (see Methods for details) for HO–C=O (▵), HO–C=O (□), and HO–C=O (○). The curves are the results of nonlinear least-square fitting of the computational data to Morse potentials. The strongest hydrogen-bonding interaction occurs at 2.94 Å with −11.6 kJ/mol for HO–C=O, 2.87 Å with −18.8 kJ/mol for HO–C=O, and 2.75 Å with −32.1 kJ/mol for HO–C=O.