TABLE 4.
Calculated hydrogen-bonding properties of a COOH group interacting with polar amino acid side chains
| Structure* | Amino acid* | No. of H-bond† | H-bond length† (Å) | H-bond angle† (°) | H-bond energy‡ (kJ/mol) | C=O frequency‡ (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
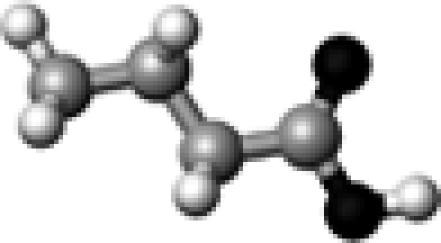 |
N/A | 0 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1776.4 |
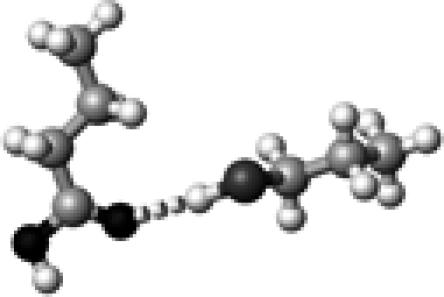 |
Cys–1 | ∼0 | 3.60 | 175.8 | 5.9 | 1759.1 |
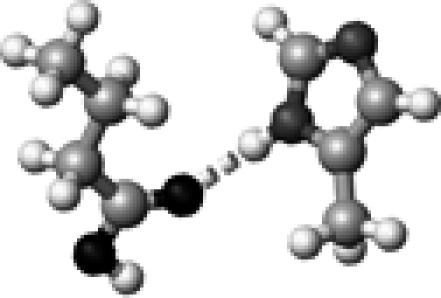 |
His–1a | 1 | 2.99 | 174.7 | 20.3 | 1748.8 |
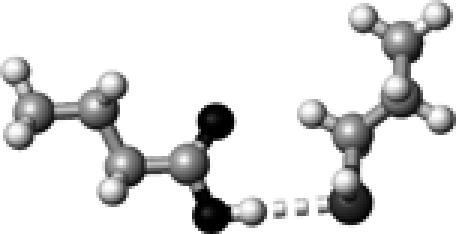 |
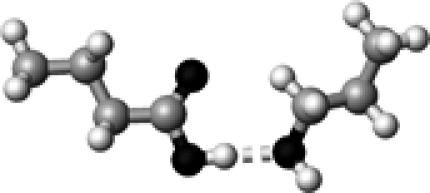
Cys–2 | 1 | 3.37 | 175.7 | 24.8 | 1746.9 |
 |
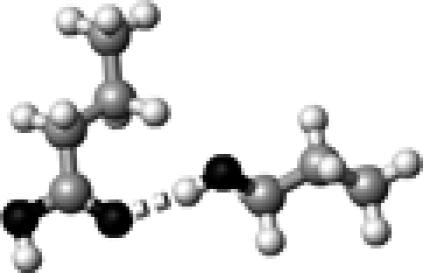
Ser–2 | 1 | 2.75 | 177.7 | 31.9 | 1744.2 |
 |
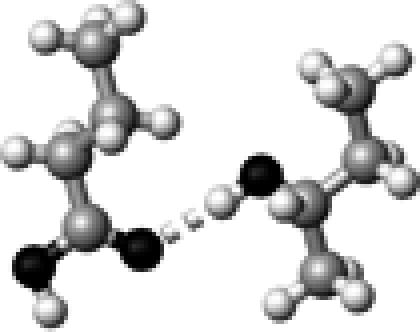
Ser–1 | 1 | 2.89 | 171.3 | 17.6 | 1743.7 |
 |
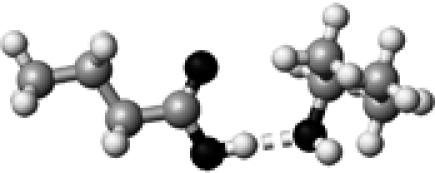
Thr–1 | 1 | 2.90 | 172.8 | 17.4 | 1742.6 |
 |
Thr–2 | 1 | 2.75 | 176.4 | 32.2 | 1739.4 |
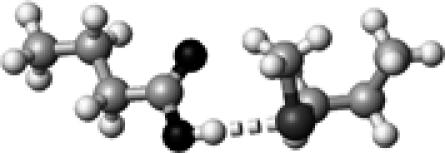 |
Met | 1 | 3.30 | 174.7 | 21.2 | 1738.2 |
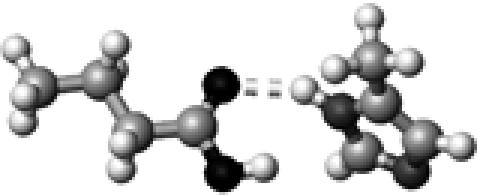 |
His–1b | 1 | 2.93 | 151.8 | 21.2 | 1736.3 |
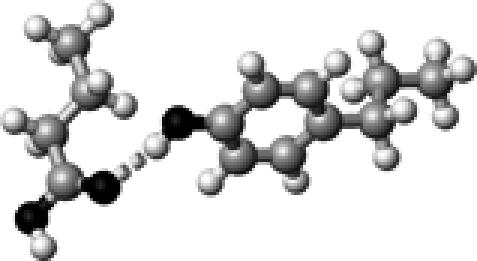 |
Tyr–1 | 1 | 2.84 | 173.6 | 24.0 | 1736.2 |
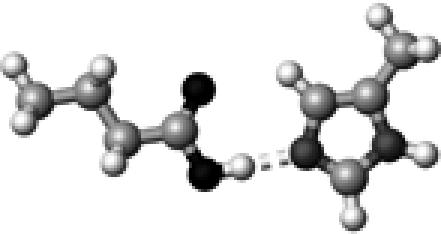 |
His–2 | 1 | 2.77 | 178.5 | 45.3 | 1733.4 |
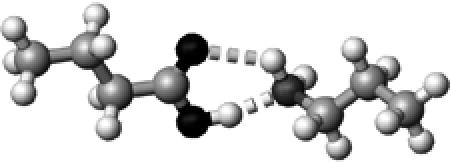 |
Lys | ∼1.5 | 2.73,2.99 | 166.3,126.5 | 44.8 | 1726.2 |
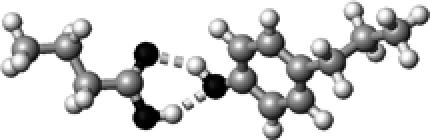 |
Tyr | ∼1.5 | 2.77,2.72 | 154.0,145.0 | 37.5 | 1717.8 |
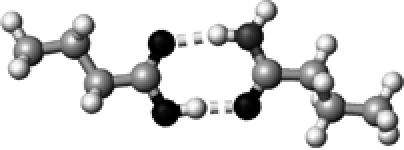 |
Asn/Gln | 2 | 2.68,2.88 | 173.4,168.0 | 61.2 | 1709.9§ |
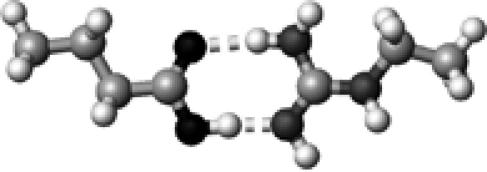 |
Arg | 2 | 2.65,2.90 | 175.3,173.2 | 70.4 | 1704.8 |
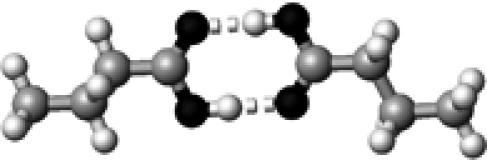 |
Asp/Glu | 2 | 2.69,2.69 | 178.9,179.4 | 63.7 | 1702.9§ |
The structures presented here are optimized using the B3LYP/6-31G(d) method. There are four shades of color code for atoms: the darkest for oxygen atoms, the dark gray for nitrogen and sulfur atoms, the light gray for carbon atoms, and white for hydrogen atoms. The dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. His–1 indicates that the carbonyl oxygen of a COOH group forms a hydrogen bond, whereas His–2 designates that the hydroxyl hydrogen of a COOH group forms a hydrogen bond. The same notation is used for other amino acids.
The hydrogen-bond length is measured between the heavy atoms of a pair of hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor. When two hydrogen bonds are formed, the first value is for hydroxyl oxygen and the second value is for carbonyl oxygen.
The vibrational frequencies were calculated using the B3LYP/6-31G(d) method on optimized structures. The energy was computed using the B3LYP/6-311+G(2d,p) method.
The C=O stretching frequency was initially coupled to that of its hydrogen-bond partner in forms of asymmetric and symmetric C=O stretching of two carbonyl groups. To remove this vibrational coupling, we isotopically labeled the hydrogen-bond partner (18O=C–15N2H2 for Asn/Gln, and 18O=C–18O2H for Asp/Glu), then calculate the C=O stretching frequency of the COOH group (butyric acid).
