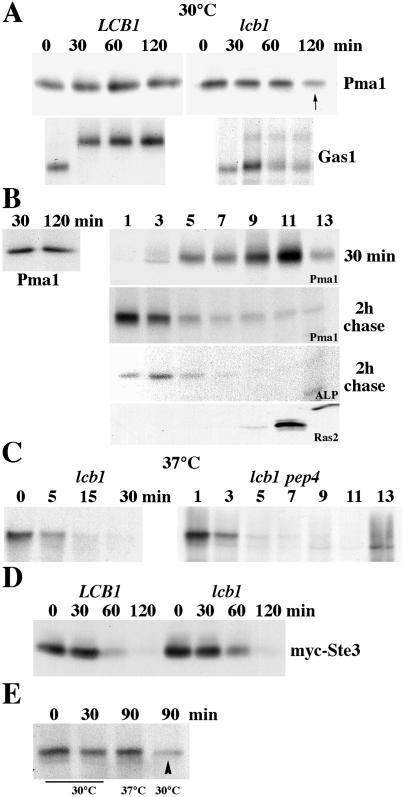
Figure 4.
Cell surface delivery and endocytosis in lcb1-100 cells. (A) Pulse–chase analysis. LCB1+ (RH3435) and lcb1-100 cells (RH3804) were metabolically labeled at 30°C for 5 min and chased for various times. Immunoprecipitation of Pma1 and Gas1 was normalized to acid-precipitable cpm and was analyzed by SDS/PAGE and fluorography. lcb1-100 results are representative of six independent experiments. (B) Newly synthesized Pma1 is delivered to and removed from the plasma membrane at 30°C. lcb1-100 pep4 (WQY7) cells were pulse-labeled at 30°C for 5 min and chased for 30 min and 2 h. (Left) Pma1 was immunoprecipitated from total lysate. (Right) Cell lysate was fractionated on density gradients. Pma1 and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were immunoprecipitated from gradient fractions. Ras2 localization was determined by Western blotting of gradient fractions. (C) Rapid vacuolar degradation of newly synthesized Pma1 at 37°C. lcb1-100 cells were metabolically labeled at 37°C for 5 min and chased for various times. (Left) Pma1 IP. (Right) lcb1-100 pep4 cells were pulse-labeled and chased for 30 min at 37°C. Lysate was fractionated on density gradients and Pma1 was immunoprecipitated from gradient fractions. (D) Endocytosis of Ste3. LCB1+ and lcb1-100 cells bearing GAL-STE3-myc (pSL2015) were grown in medium with galactose at 30°C. Cells were harvested at various times after addition of glucose (3%) and Ste3-myc was analyzed by Western blotting. (E) Stability of cell surface Pma1 in lcb1-100. Cells were pulse-labeled at 30°C for 5 min and chased for 30 min. Cells were then divided and the chase was continued for 60 min at 30°C or 37°C. Pma1 was immunoprecipitated from lysate. Cell surface Pma1 remains stable after chase at 37°C but not 30°C (arrowhead).