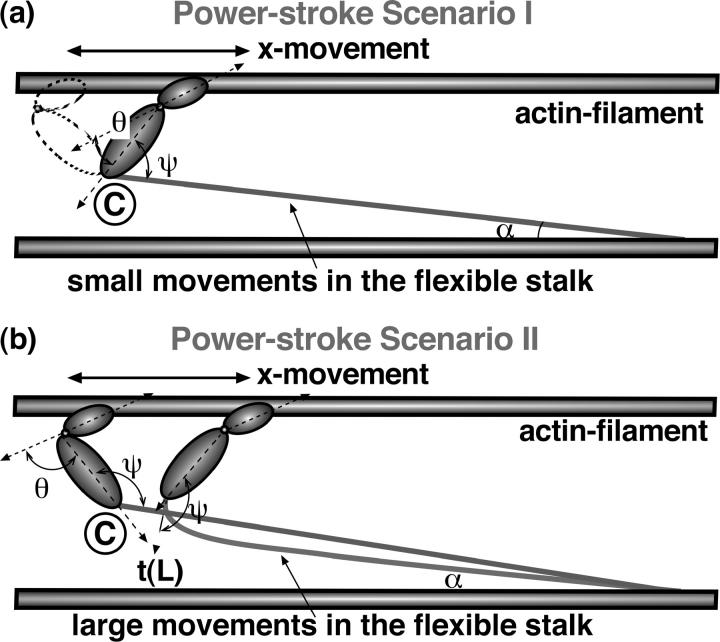
FIGURE 3.
Two powerstroke scenarios. (a, scenario I) Myosin motor rotates with respect to point C. The angles, ψ and θ, change during the powerstroke. The light-chain filament is largely undeformed during the powerstroke, except for a small deflection when the myosin motor is almost perpendicular to the actin filament. This deflection energy is accounted for in our model. (b, scenario II) In the second scenario, the angle ψ is fixed during the powerstroke. The motion is achieved through bending the stalk domain, and the subsequent relaxation of the bending energy drives the thin filament forward.