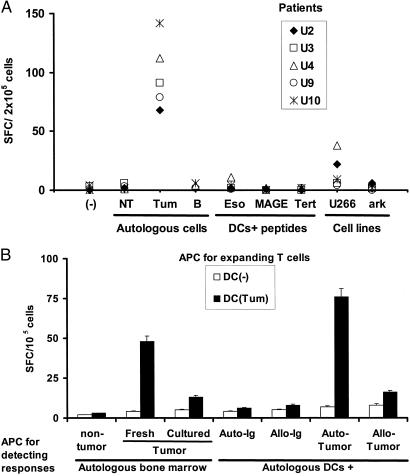
Figure 4.
Nature of antigens by tumor-specific killer T cells. (A) T cells from HLA A2-positive patients expanded by using DCs loaded with antibody-coated tumor cells were tested for the recognition of autologous tumor or nontumor fractions from the marrow, purified autologous B cells, HLA A2.1-positive (U266) or negative (ark) myeloma cell lines, or HLA A2.1-restricted peptides derived from MAGE-3, h-TERT, or NY-ESO-1, using peptide-pulsed DCs as APCs (effector/APC ratio, 50:1). IFN-γ-producing cells (SFCs) were quantified in an ELISPOT assay. Data are shown as SFC/2 × 105 cells per well. (B) T cells (105 cells per well) from a patient with IgG myeloma expanded by using unpulsed DCs or DCs loaded with antibody-coated tumor cells were tested for the recognition of autologous CD138+ tumor [either fresh or cultured ex vivo in the presence of IL-6 (1,000 units/ml) and granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (10 ng/ml) for 2 days] or nontumor cells (CD138-ve) from the bone marrow or autologous DCs pulsed with purified tumor-derived circulating Ig, allogeneic Ig, or DCs fed with autologous or allogeneic tumor cells (tumor/DC ratio, 1:1) as APCs. Effector cells were cultured overnight with APCs (effector/APC ratio, 50:1) and IFN-γ-producing cells (SFCs) quantified by an ELISPOT assay. Data are representative of experiments on two separate patients.