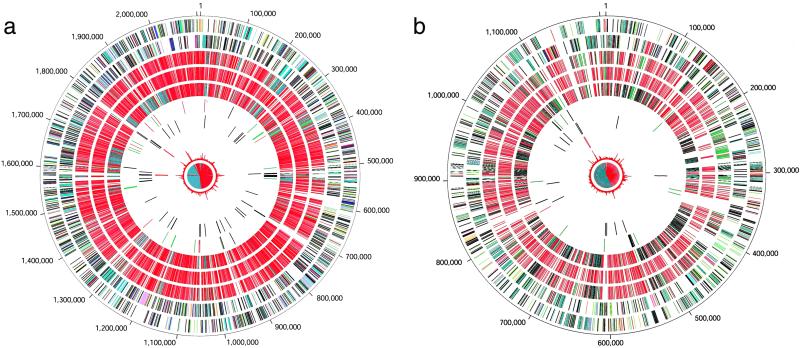
Figure 1.
Circular representation of the two chromosomes of B. suis strain 1330. The outer circle shows predicted coding regions on the plus strand color-coded by role categories: salmon, amino acid biosynthesis; light blue, biosynthesis of cofactors, prosthetic groups and carriers; light green, cell envelope; red, cellular processes; brown, central intermediary metabolism; yellow, DNA metabolism; green, energy metabolism; purple, fatty acid and phospholipid metabolism; pink, protein fate/synthesis; orange, purines, pyrimidines, nucleosides, nucleotides; blue, regulatory functions; gray, transcription; teal, transport and binding proteins; black, hypothetical and conserved hypothetical proteins. Second circle, predicted coding regions on the minus strand color-coded by role categories. Third circle, top hits to S. meliloti, according to replicon: red, main chromosome; green, plasmid pSymA; gray, plasmid pSymB. Fourth circle, top hits to M. loti, according to replicon: red, main chromosome; green, plasmid pMLa; gray, plasmid pMLb. Fifth circle, top hits to A. tumefaciens, according to replicon: red, circular chromosome; gray, linear chromosome; green, plasmid pAtC58; blue, plasmid pTiC58. Sixth circle, locations of B. suis-specific regions greater than 100 base pairs, green; B. melitensis-specific regions greater than 100 base pairs, red; and transposase genes, black. Seventh circle, tRNAs in brown. Eighth circle, rRNA operons in red. Ninth circle, atypical nucleotide composition curve in red. Tenth circle, GC-skew curve in red/black.