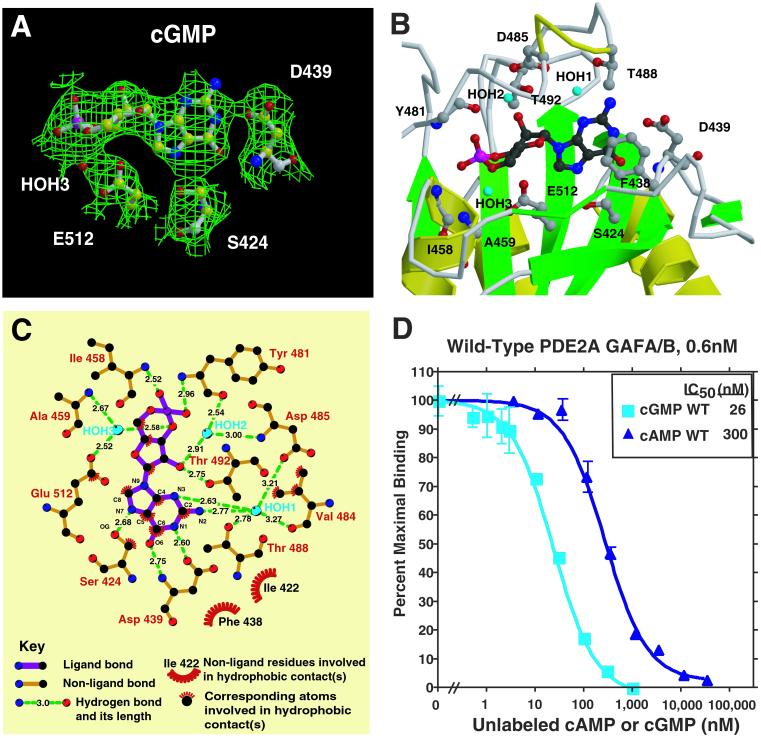
Figure 3.
cGMP binding by PDE2A. (A) Electron density in a Sigma A-weighted omit map contoured at the 1.0 σ level shown together with cGMP bound to the GAF B domain of PDE2A. The density at the phosphate is 5 σ. Also shown is the critical Asp D439 that interacts with the guanine base with both its side-chain carboxylate and main-chain amino groups. This figure was prepared with BOBSCRIPT (31) and rendered with RASTER3D (32). (B) Close-up view of the cGMP-binding site in GAF B. Shown are six side chains that make hydrogen bonds to the cGMP, one that stacks with the guanine ring, and two that make backbone amide contacts. Helix α4 and strand β3′ are depicted as coils for visibility of the cGMP. This figure was made with MOLSCRIPT (31) and RASTER3D (32). (C) Diagram showing all of the close interactions between cGMP and GAF B. The diagram was produced with LIGPLOT (33). The general features of cGMP binding in the GAF B structure are consistent with many of the predictions made from binding studies of PDE2 and PDE6 with cyclic nucleotide analogues. These studies suggested that cGMP would be bound in the anti-conformation, that contacts are made to C6, N1, and C2 amino group of the guanine ring and 2′O of the ribose ring, and that there are similar or identical types of contacts to the exocyclic oxygens (21, 26, 34). (D) cGMP and cAMP competition binding curves [against (3H)cGMP] for the wild-type regulatory segment of mouse PDE2A. A nitrocellulose filter-binding assay was used (18). Protein concentration was 0.6 nM.