Figure 3.
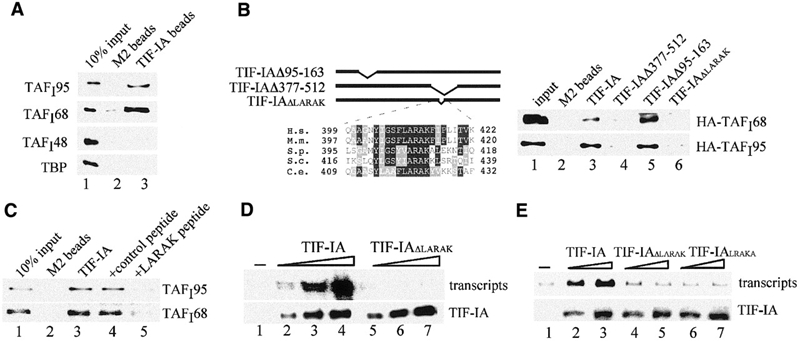
A conserved motif (LARAK) mediates the interaction of TIF-IA with TAFI95 and TAFI68. (A) Pull-down assay. Bead-bound Flag-tagged TIF-IA was incubated with extracts from Sf9 cells overexpressing HA-tagged TAFI48, TAFI68, TAFI95 or TBP, respectively. Proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE, and TAFIs were visualized on western blots using α-HA antibodies (lane 3). M2 beads saturated with the Flag epitope peptide were used as a control (lane 2). (B) The LARAK motif mediates the interaction of TIF-IA with TAFI68 and TAFI95. Flag-tagged TIF-IA (lane 3), TIF-IAΔ377–512 (lane 4), TIF-IAΔ95–163 (lane 5) and TIF-IAΔLARAK (lane 6) were incubated with HA-tagged TAFI68 or TAFI95. TIF-IA was immunoprecipitated, and associated TAFIs were visualized on western blots. A scheme of the mutants and a sequence alignment of the LARAK domain of TIF-IA homologues are shown above. H.s., Homo sapiens; M.m., Mus musculus; S.p., Schizosaccharomyces pombe; S.c., Saccharomyces cerevisiae; C.e., Caenorhabditis elegans. (C) A synthetic peptide (LARAK) blocks the interaction between TIF-IA and TIF-IB/SL1. Immobilized TIF-IA was incubated at 4°C for 4 h with partially purified TIF-IB/SL1 in the absence (lane 3) or presence of 200 ng control peptide (EHLWKKLQDPSNPAI, lane 4) or LARAK peptide (YIGSFLARAKFITVKSC, lane 5) in 250 μl of buffer AM-100/0.5% NP-40. After stringent washing, bound TIF-IB/SL1 was analyzed on immunoblots with α-TAFI95 or α-TAFI68 antibodies. (D) The LARAK motif is essential for TIF-IA activity. In vitro transcription assays contained nuclear extracts from density-arrested FM3A cells and no exogenous TIF-IA (lane 1) or 15, 30 and 50 ng of wild-type TIF-IA (lanes 2–4) or TIF-IAΔLARAK (lanes 5–7). The amounts of recombinant TIF-IA added to the reactions was monitored on western blots with α-Flag antibodies (lower panel). (E) Deletion or permutation of the LARAK motif abrogates TIF-IA activity in vivo. NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with 2.5 μg of the rDNA reporter plasmid and 1 or 2 μg of pBK-CMV-Flag-TIF-IA (lanes 2 and 3), pBK-CMV-Flag-TIF-IAΔLARAK (lanes 4 and 5) or pBK-CMV-Flag-TIF-IALRAKA (lanes 6 and 7). Transcripts from the rDNA reporter were monitored on northern blots. TIF-IA expression levels were monitored on western blots with α-Flag antibodies (lower panel).
