Figure 4.
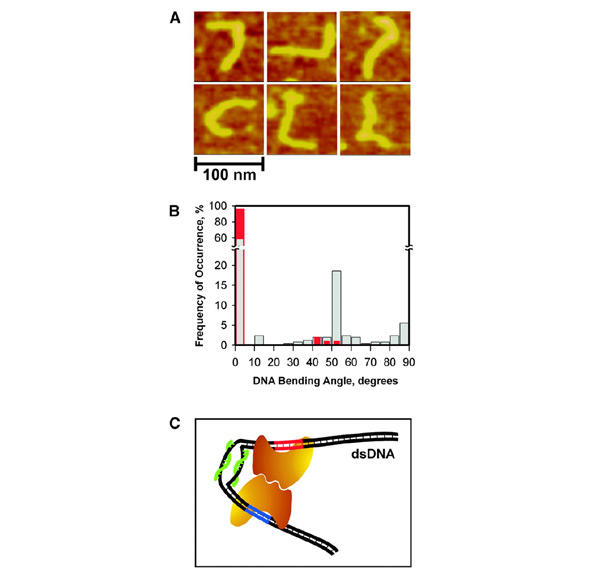
The PNA-induced dsDNA bending. (A) AFM images of 345-bp dsDNA fragments (pD5-10F) complexed with pcPNAs 125 bp apart from DNA terminus (the shortest arm). The double-duplex invasion of pcPNAs (Lohse et al., 1999; Izvolsky et al., 2000; Demidov et al., 2002) produces a hinge-like distortion within the DNA duplex seen here as sharp bends of various angles. (B) Histograms of the DNA bending angles measured from AFM images of PNA–DNA complexes (grey bars) and control with 'naked' DNA (red bars). (C) Model for the PNA-assisted dimerization of two enzyme molecules (the bean-like shapes), one bound to its primary recognition site on dsDNA (red) and the other to the site with degenerate recognition sequence (blue). This cartoon schematically illustrates our concept of the directed, smallsize (∼30–60 bp) DNA looping based on the local dynamic bending of dsDNA due to the double-duplex invasion of a pcPNA pair (green).
