Abstract
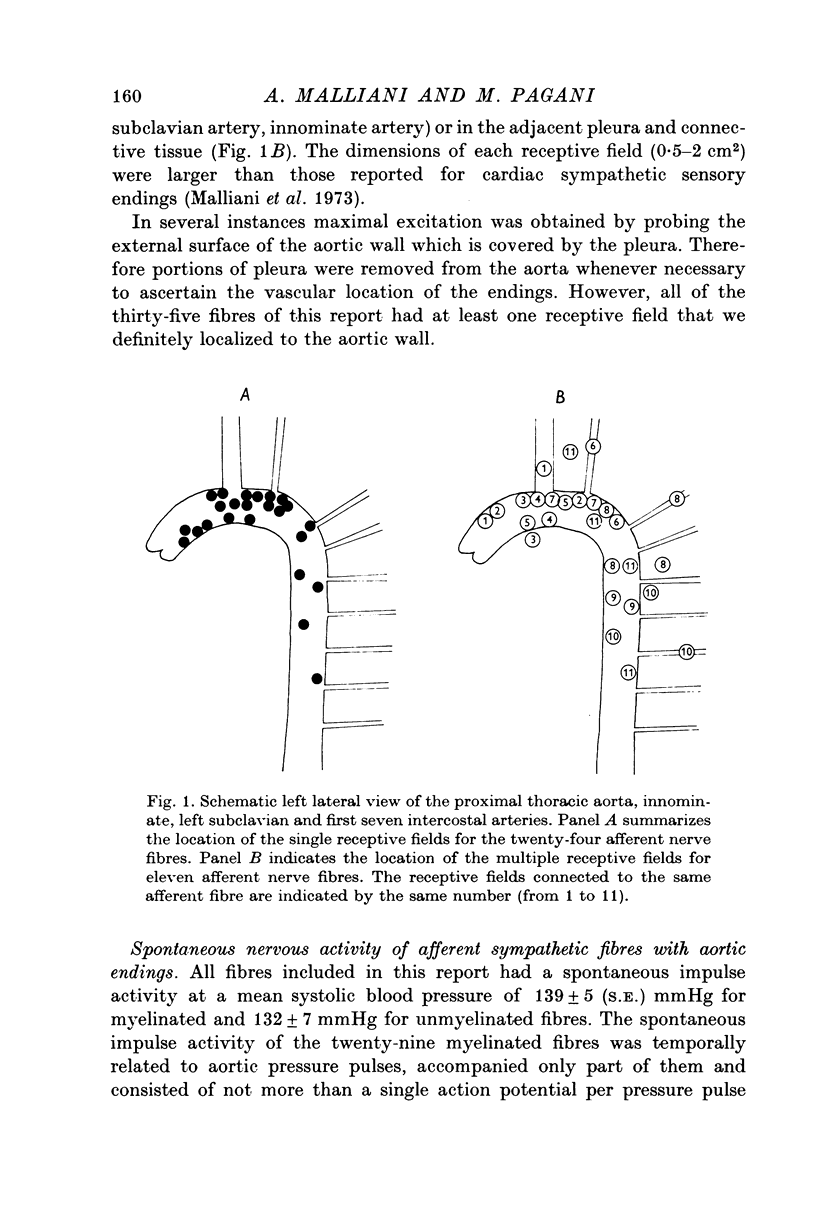
1. We recorded the electrical impulse activity of thirty-five single afferent fibres with aortic endings isolated from the third to the sixth left thoracic sympathetic rami communicantes of anaesthetized cats. The endings of each fibre were localized by mechanical probing of the opened aorta at the end of each experiment. 2. Twenty-four fibres had a single aortic receptive field. Eleven fibres had several and distinct receptive fields (from two to four): they were usually located in nearby aortic areas or, in addition, in other proximal portions of the arterial tree or in the adjacent pleura and connective tissue. 3. Twenty-nine fibres had conduction velocities ranging between 5 and 27 m/sec (Group Adelta), while six fibres had conduction velocities between 0-2 and 1-2m/sec (Group C). 4. The spontaneous impulse activity was in phase with the aortic pressure pulse and consisted of not more than one impulse per pressure pulse. It was increased during increases in aortic pressure and, conversely, decreased during decreases in aortic pressure. In vivo and post mortem studies showed that these mechanoreceptors had an impulse activity which rapidly adapted during sustained stimuli. They thus seem to signal pulsatile aortic stretch. 5. These aortic sympathetic afferents are likely to be part of a nervous pathway through which pressor reflexes, exhibiting positive feed-back characteristics, can elicited.
Full text
PDF


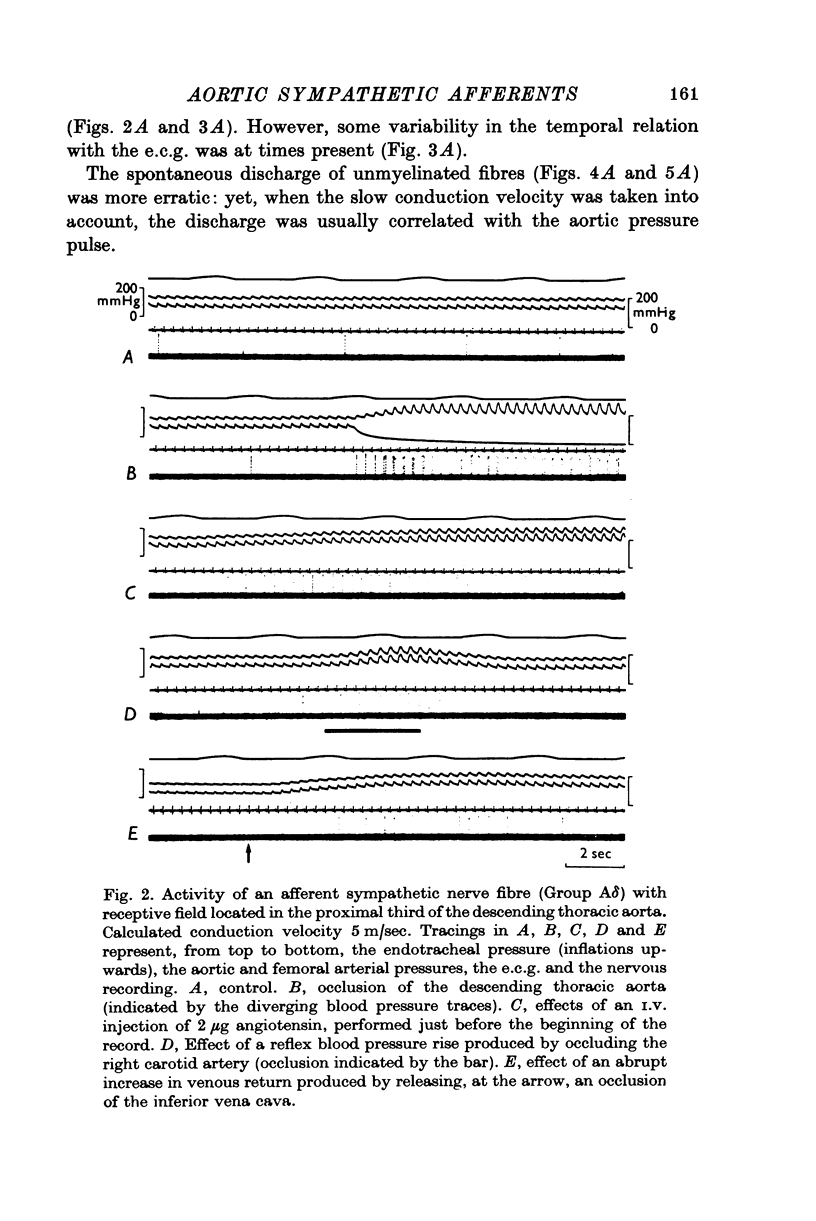
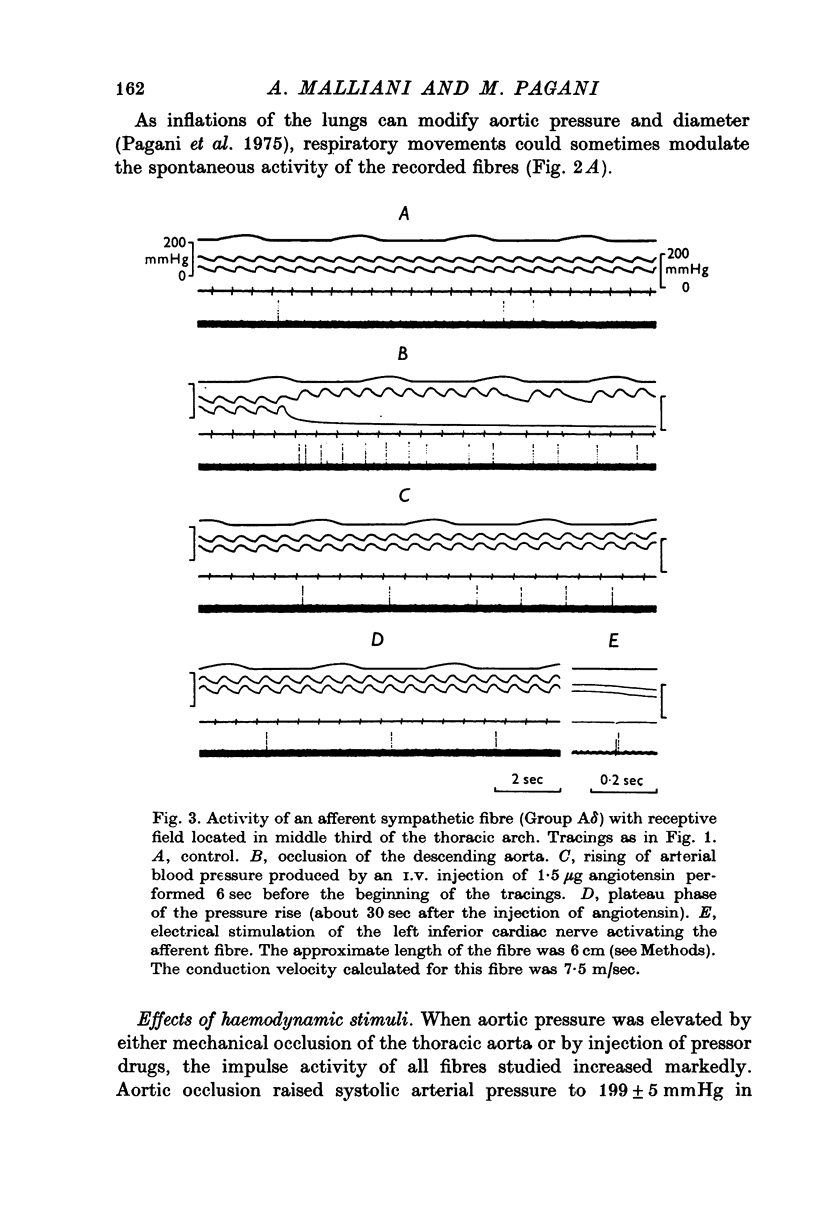

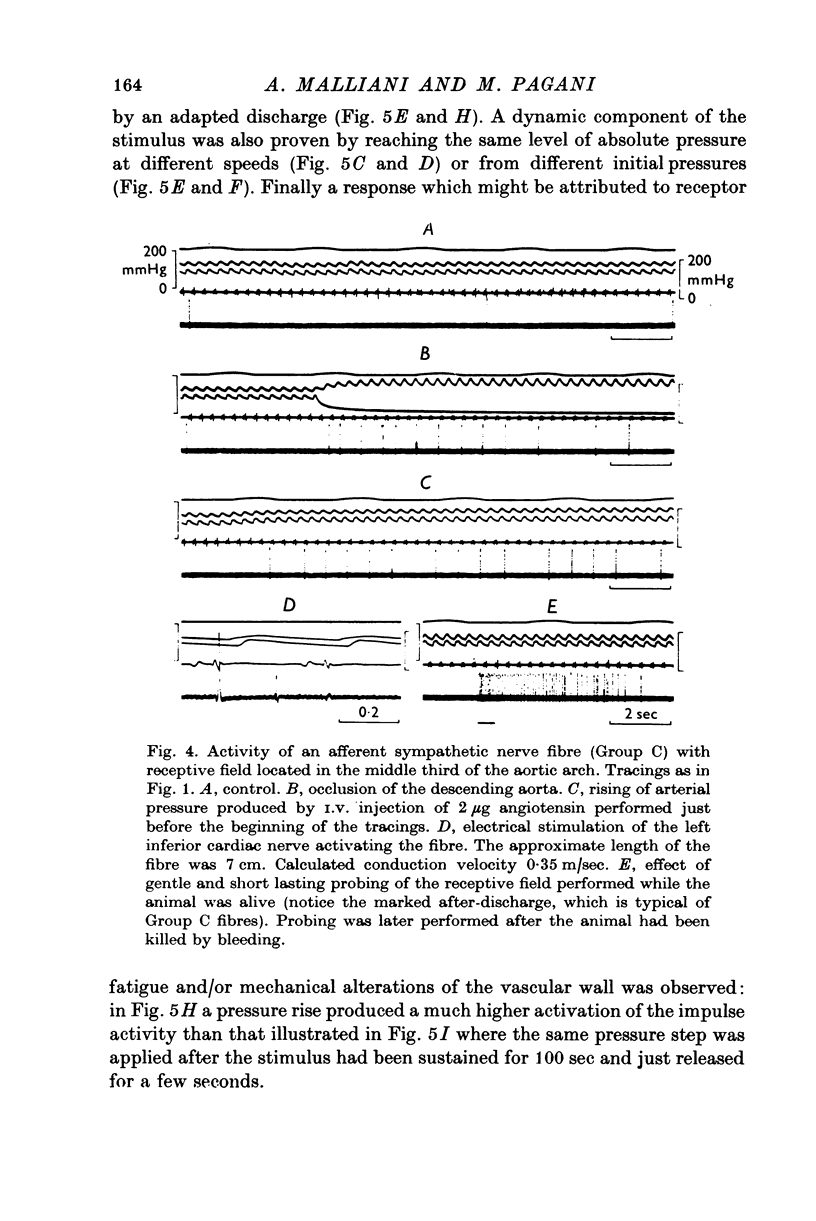




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews C. J., Andrews W. H., Orbach J. A sympathetic reflex elicited by distension of the mesenteric venous bed. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):119–131. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainbridge F. A. The influence of venous filling upon the rate of the heart. J Physiol. 1915 Dec 24;50(2):65–84. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop V. S., Lombardi F., Malliani A., Pagani M., Recordati G. Reflex sympathetic tachycardia during intravenous infusions in chronic spinal cats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jan;230(1):25–29. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M., Malliani A. Spinal sympathetic reflexes initiated by coronary receptors. J Physiol. 1971 Feb;212(3):685–705. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P. D. Spinal autonomic afferents in elicitation of tachycardia in volume infusion in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):303–308. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R., TORRANCE R. W. Afferent fibres of the stellate ganglion. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Jul;44:271–281. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess G. L., Zuperku E. J., Coon R. L., Kampine J. P. Sympathetic afferent nerve activity of left ventricular origin. Am J Physiol. 1974 Sep;227(3):543–546. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lioy F., Malliani A., Pagani M., Recordati G., Schwartz P. J. Reflex hemodynamic responses initiated from the thoracic aorta. Circ Res. 1974 Jan;34(1):78–84. doi: 10.1161/01.res.40.4.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi F., Malliani A., Pagani M. Nervous activity of afferent sympathetic fibers innervating the pulmonary veins. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 20;113(1):197–200. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Brown A. M. Reflexes arising from coronary receptors. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 1;24(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Lombardi F., Pagani M., Recordati G., Schwartz P. J. Spinal cardiovascular reflexes. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 11;87(2-3):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90421-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malliani A., Recordati G., Schwartz P. J. Nervous activity of afferent cardiac sympathetic fibres with atrial and ventricular endings. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):457–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagani M. Proceedings: Afferent sympathetic nerve fibres with aortic endings. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(2):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagani M., Schwartz P. J., Banks R., Lombardi F., Malliani A. Reflex responses of sympathetic preganglionic neurones initiated by different cardiovascular receptors in spinal animals. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 22;68(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90391-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagani M., Schwartz P. J., Bishop V. S., Malliani A. Reflex sympathetic changes in aortic diastolic pressure-diameter relationship. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):286–290. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y. Afferent aortic nerve fibers with their pathways in cardiac sympathetic nerves. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):990–995. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Uchida Y., Kamisaka K. Distribution and responses of the cardiac sympathetic receptors to mechanically induced circulatory changes. Jpn Heart J. 1969 Jan;10(1):70–81. doi: 10.1536/ihj.10.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. C. Cardiac pain: anatomic pathways and physiologic mechanisms. Circulation. 1957 Oct;16(4):644–655. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.4.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


