Figure 1.
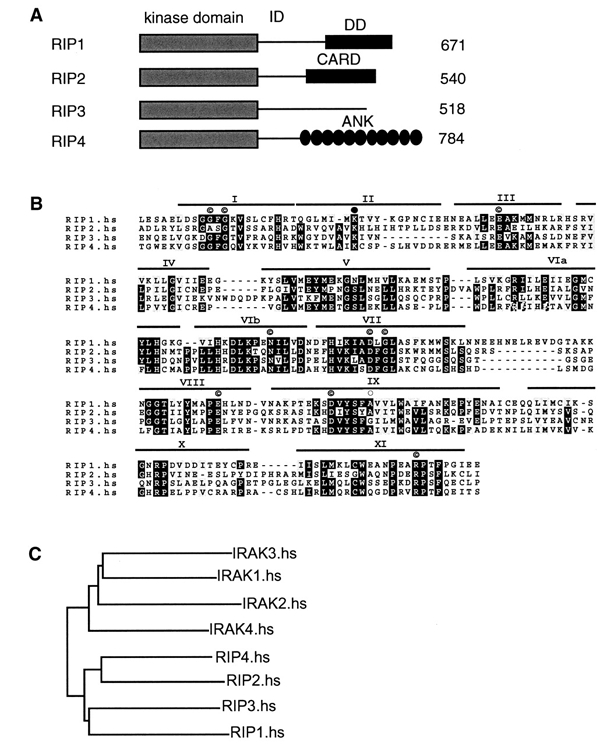
RIP4 is a novel member of the RIP family of kinases. (A) Domain organization of RIP family members. All members share a homologous N-terminal kinase domain. RIP1 and RIP2 have C-terminal DD and CARD motifs, respectively, whereas the C-terminus of RIP3 lacks obvious sequence homology to known proteins in public databases. RIP4 has C-terminal ankyrin repeats. (B) Sequence alignment of the kinase domains of RIPs. Black and gray shading indicate 75% amino acid sequence identity and similarity, respectively. I–XI represent conserved modules (Hanks and Hunter, 1995). Indicated are residues conserved in 95% of the kinases (©), residues important for ATP binding (filled circle) and the Gly residue present in RIP3 (open circle) that is conserved in 95% of all kinases but is substituted into Ala in RIP1, RIP2 and RIP4. (C) Phylogenic tree of the kinase domain of human RIPs and IRAKs.
