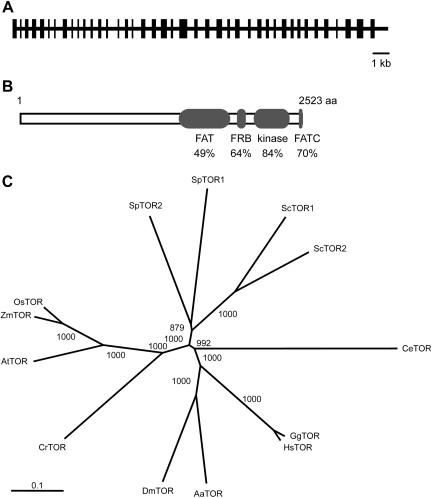
Figure 3.
TOR is conserved in Chlamydomonas. A, Structure of CrTOR gene predicted from the Chlamydomonas nuclear genome. The intron and exon positions were deduced by comparison of genomic and partial cDNA sequences, and homology analysis with other TOR proteins. The black rectangles indicate the position of the protein-coding regions. B, Comparison of the CrTOR protein sequence to AtTOR. Values indicate the percentage of identity with the corresponding domain sequence of CrTOR. FAT, FRB, kinase, and FATC domains correspond to residues 1,374 to 1,924; 1,961 to 2,055; 2,124 to 2,372; and 2,493 to 2,523, respectively. C, Phylogenetic relationship of TOR from Chlamydomonas and representative organisms. The phylogenetic tree was constructed with full-length TOR amino acid sequences and aligned using the ClustalW program. The bootstrap values represent 1,000 replications. Sc, S. cerevisiae; Sp, Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Os, O. sativa; Zm, Zea mays; At, Arabidopsis; Cr, C. reinhardtii; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Aa, Anopheles aedes; Hs, Homo sapiens; Gg, Gallus gallus; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans.