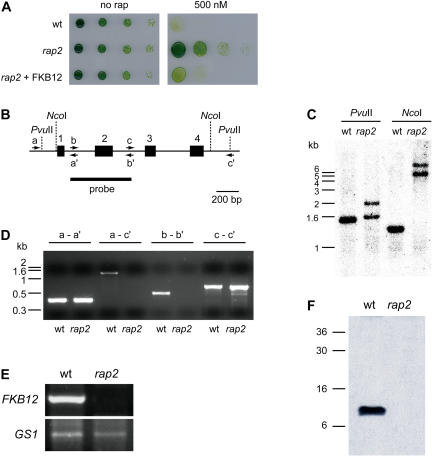
Figure 4.
Characterization of the Chlamydomonas rap2 mutant strain. A, rap2 mutant cells are rapamycin insensitive. Serial dilutions of wild-type, rap2, and rap2 cells transformed with the pJC20 plasmid on TAP plates containing 500 nm rapamycin (500 nm) or drug vehicle (no rap). Growth was recorded after 4 d incubation at 25°C under continuous illumination. B, Structure of the FKB12 gene from Chlamydomonas. The closed rectangles and numbers (1–4) indicate the four exons of the FKB12 gene. Primers used for the PCR analysis of the FKB12 gene (see D) are represented by arrows and letters. Restriction sites for NcoI and PvuII restriction enzymes are shown by dotted lines. C, Southern-blot analysis of genomic DNA from the rap2 mutant compared to the wild-type strain. Ten micrograms of DNA were digested with NcoI or PvuII. The blot was hybridized with an FKB12 probe obtained by PCR (see B). D, PCR analysis of the FKB12 gene from wild-type and rap2 cells. Letters indicate the different set of primers used for PCRs reactions (see B for the position of different primers). E, RT-PCR analysis of FKB12 in wild-type and rap2 mutant cells. Semiquantitative RT-PCR was terminated after 20 cycles for FKB12 and 24 cycles for GS1. The cytosolic gene, GS1, whose expression is not expected to change in the rap2 mutant, was used as an internal control for RNA level. F, Western blot of FKB12 from wild-type and rap2 strains. Fifteen micrograms of total protein obtained from wild-type and rap2 cells were resolved on 15% polyacrylamide gels, blotted, and incubated with anti-FKB12 antibodies.