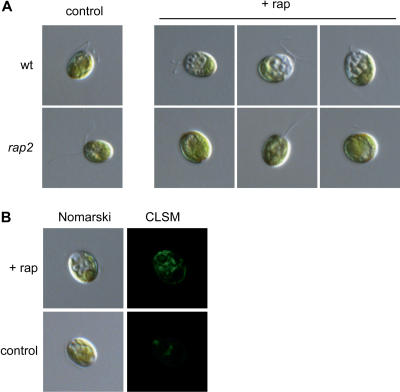
Figure 9.
Rapamycin-induced vacuolization in Chlamydomonas. A, Nomarski micrographs of wild-type and rap2 mutant living cells treated with 500 nm rapamycin (+rap) or drug vehicle (control) for 24 h. Cultures were synchronized by alternating light and dark (12 h/12 h) cycles before rapamycin addition. B, Nomarski and CLSM images of a wild-type living cell treated with rapamycin (+rap) or drug vehicle (control) for 24 h. Cells were incubated with the pH-sensitive dye LysoSensor Green DND-189, which produces fluorescent foci mainly in the region of the cell containing vacuoles.