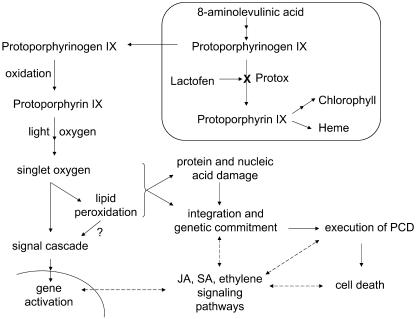
Figure 9.
Working model for lactofen-induced cell death and defense gene activation. Lactofen initiates singlet oxygen generation by inhibition of Protox within chloroplasts/etioplasts/mitochondria (described in detail in the introduction). Singlet oxygen initiates lipid peroxidation (Hess, 2000) and possible signaling cascades that stimulate gene activation (op den Camp, 2003) and commitment to the execution of PCD (Wagner et al., 2004; Foyer and Noctor, 2005). Possible associations and positive/negative influences on cell death by various defense-signaling pathways, such as those for jasmonic acid (JA), salicylic acid (SA), and ethylene (Danon et al., 2005), are shown with dotted arrows. Since the lactofen-induced defense reactions discussed here are predominantly local, for simplicity distal or systemic effects have not been included.