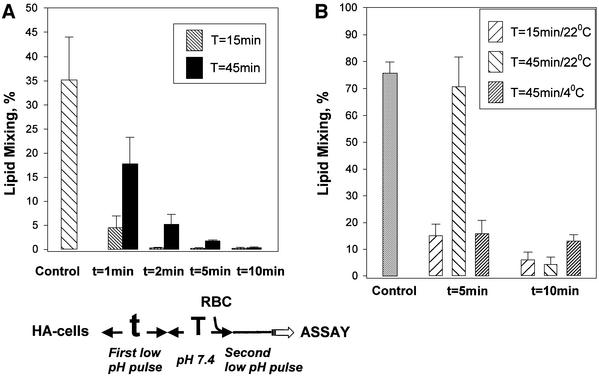
Fig. 3. Recovery of low-pH-activated HA molecules at 37 and 4°C evaluated by fusion inactivation assay. (A) Rapid loss of reversibility at 37°C. X31 HA-cells at 37°C were first treated with an AP (pH 4.9 for 1, 2, 5 or 10 min) applied in the absence of target membrane. The cells were incubated at pH 7.4 for 0 or 30 min, incubated with RBCs for 15 min and treated with an FTP (1 min, pH 4.9). The time interval between the end of the AP and the beginning of the FTP was either 15 or 45 min. The ‘control’ bar presents the results of the control experiment, in which only the FTP was applied to the HA-cells, with bound RBCs untreated with an AP. The final extents of lipid mixing were measured by fluorescence microscopy. (B) HA recovery is blocked at 4°C. X31 HA-cells at 22°C were first treated with an AP (pH 4.9 for 5 or 10 min) applied in the absence of target membrane. The cells were incubated at pH 7.4 for 0 or 30 min, incubated with RBCs for 15 min and treated with an FTP (2 min, pH 4.9, 22°C). During the total time interval, either 15 or 45 min, between the end of the AP and the beginning of the FTP, cells were kept at either 22 or 4°C. In the experiment represented in the ‘control’ bar, the FTP (2 min, pH 4.9, 22°C) was applied to the HA-cells, with bound RBCs untreated with an AP.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.