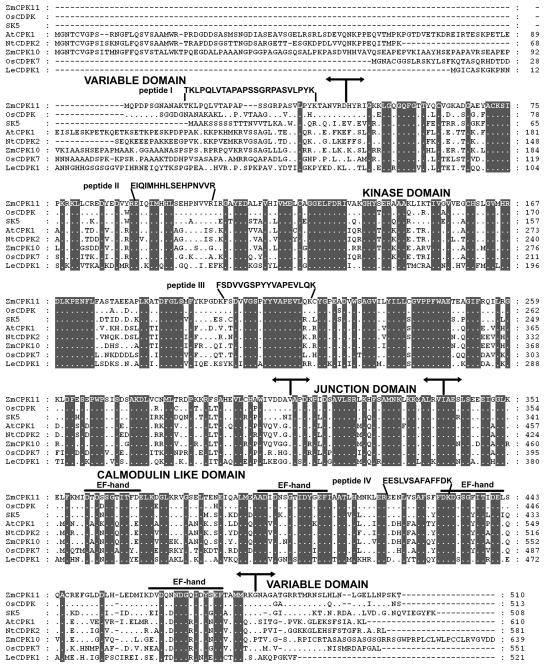
Figure 1.
The deduced amino acid sequence of ZmCPK11 is aligned with OsCDPK (accession no. AY144497) from rice, SK5 (CDPKα) from soybean (Harper et al., 1991), AtCPK1 from Arabidopsis (Harper et al., 1993), NtCDPK2 from tobacco (Romeis et al., 2001), ZmCPK10 from maize (Murillo et al., 2001), OsCDPK7 from rice (Saijo et al., 2000), and LeCDPK1 from tomato (Chico et al., 2002). Sequences were aligned with the PileUp program from the Genetics Computer Group suite of programs. Numbers indicate amino acid residues in the sequences. Dots indicate amino acids identical to those corresponding to the ZmCPK11 sequence. Shaded backgrounds indicate amino acids identical throughout. Dashes indicate gaps introduced to maximize the alignment. The boundaries of the variable, kinase, autoregulatory, and calmodulin-like domains are shown by arrows. The four Ca2+-binding EF-hand motifs in the calmodulin-like domain are overlined. Peptide (I–IV) data obtained from microsequencing are shown above the deduced amino acid sequence of ZmCPK11.