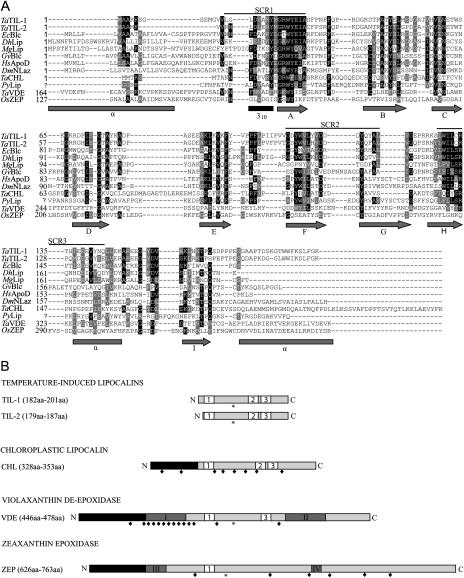
Figure 1.
Structure of plant lipocalins and lipocalin-like proteins. A, Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of wheat lipocalins with a select set of related lipocalins. Identical residues are in black and similar residues are in gray. The three SCRs that provide a signature for lipocalins are indicated. The secondary structure predicted from already published models (Bishop et al., 1995; Peitsch and Boguski, 1990) is presented under the alignment. Arrows, gray rectangles, and black rectangle represent β-strands, α-helix, and the 310 α-helix, respectively. B, Schematic representation of plant lipocalins. Plant lipocalins and lipocalin-like proteins can be classified in four groups. White boxes labeled 1, 2, and 3 represent the three SCRs (SCR1, SCR2, and SCR3) that characterize lipocalins. Black rectangles represent chloroplast transit peptides. Dark-gray rectangles with roman numerals represent, respectively: I, Cys-rich region; II, Glu-rich region; III, ADP-binding site; and IV, FAD-binding site. Stars and lozenges represent conserved N-glycosylation sites and conserved Cys residues, respectively.