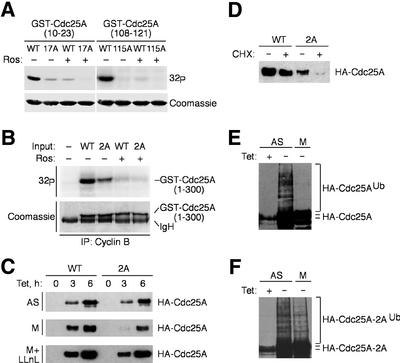
Fig. 3. Phosphorylation by cyclin B–Cdk1 uncouples Cdc25A from ubiquitylation and degradation. (A) Cyclin B–Cdk1 phosphorylates Cdc25A on Ser17 and Ser115 in vitro. Cyclin B–Cdk1 was immunoprecipitated from mitotic U-2-OS cells and assayed using the indicated GST-tagged fragments of Cdc25A containing Ser17 or Ser115, or alanine substitutions as substrates, with or without roscovitine (Ros). (B) Reduced phosphorylation of the Ser17/Ser115(2A) mutant in the context of the entire regulatory region of Cdc25A. Experimental conditions were as in (A); incorporation of 32P was reduced to ∼55% in the 2A mutant. (C) U-2-OS T-Rex cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type Cdc25A or the Ser17/Ser115(2A) mutant, treated with nocodazole (M) or left asynchronous (AS), and induced by addition of tetracycline for 3 or 6 h. Where indicated, LLnL was added to the medium at the time of the transgene induction. Cdc25A proteins were analyzed by western blotting. (D) Destabilization of Cdc25A(2A) in mitosis. U-2-OS T-Rex cells were treated as in (C), followed by addition of cycloheximide for 2 h, and Cdc25A was assessed by western blotting. (E) Cdc25A is not ubiquitylated in mitosis. Asynchronous (AS) or mitotic (M) U-2-OS/B3C4 cells transiently transfected with His-ubiquitin were kept uninduced or induced to express ectopic Cdc25A for 12 h as indicated, and processed for detection of Cdc25A-associated ubiquitin (Ub) conjugates. (F) Mutation of the cyclin B–Cdk1-targeted sites in Cdc25A restores its ubiquitylation in mitosis. U-2-OS/Cdc25A(2A) cells were treated and analyzed as in (E).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.