Figure 3.
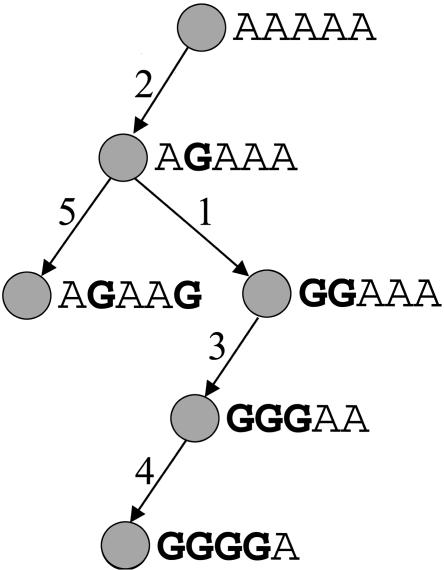
A perfect phylogeny model consists of a tree where each vertex corresponds to a haplotype and each edge corresponds to a mutation in one of the positions of the haplotype. An edge is labeled with the position of the mutation. The tree fits the perfect phylogeny model if there are no recurrent mutations and no obligate recombination events. A set of haplotypes fits the perfect phylogeny model if it satisfies the four gamete test, that is, at most three allele combinations are observed for any pair of marker positions.