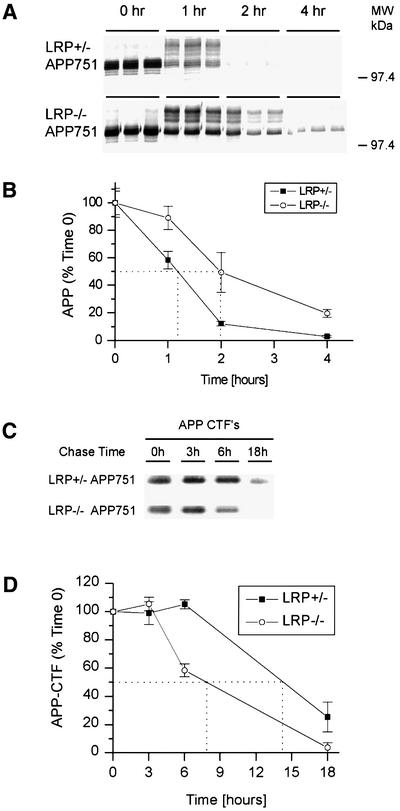
Fig. 2. Turnover of full-length APP and APP-αCTF in LRP–/– cells. LRP+/– and LRP–/– fibroblasts were pulse labeled with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 15 min and chased for 0, 1, 2 and 4 h (A). At time 0, APP consists predominantly of immature N-glycosylated species. Both the N-glycosylated and mature N- and O-glycosylated species are abundant at 1 h for both cell types. After a 2 h chase period, the APP level is dramatically reduced in LRP+/– cells and hardly detectable at 4 h. In contrast, APP can still be detected in LRP–/– cells even after a 4 h chase period. (B) The half-life was determined by quantitating the results from (A) as shown. (C) APP-αCTF turnover was determined by metabolically labeling LRP+/– and LRP–/– fibroblasts with [35S]methionine/cysteine for 1 h and chasing for 3, 6 and 18 h. Similar amounts of APP-αCTFs are present after the labeling and after the 3 h chase period in LRP+/– and LRP–/– cells. Even after an 18 h chase period, APP-αCTFs can still be detected in LRP+/– fibroblasts. However, APP-αCTFs in LRP–/– fibroblasts were almost completely degraded. (D) The half-life of APP-αCTF was determined by quantitating the results from (C) as shown. The experiment in (A) was performed in triplicate and that in (C) in duplicate, and representative experiments are shown.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.