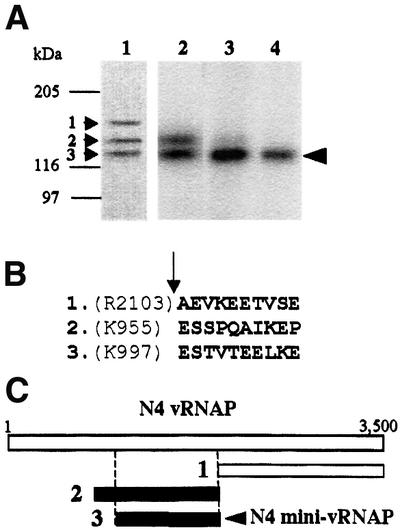
Fig. 2. Identification of the vRNAP transcriptional domain. (A) Proteolysis and catalytic autolabeling of vRNAP. Lane 1: trypsinolysis products (1, 2 and 3) visible by Coomassie R-250 staining after 10 min of digestion and transfer to PVDF. Lanes 2–4: catalytic autolabeling of proteolysis products, followed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. vRNAP was treated with trypsin for 10 min (lane 2), 1 h (lane 3) or 10 h (lane 4). Sizes and positions of protein standards are indicated. The arrowhead indicates the position of the shortest transcriptionally active proteolytic fragment. (B) N-terminal sequence obtained by Edman degradation of the proteolytic fragments shown in lane 1. The arrow indicates the position of the trypsin-cleaved peptide bond. (C) Location of the major proteolytic fragments (A) relative to the sequence of the vRNAP protein.
