Abstract
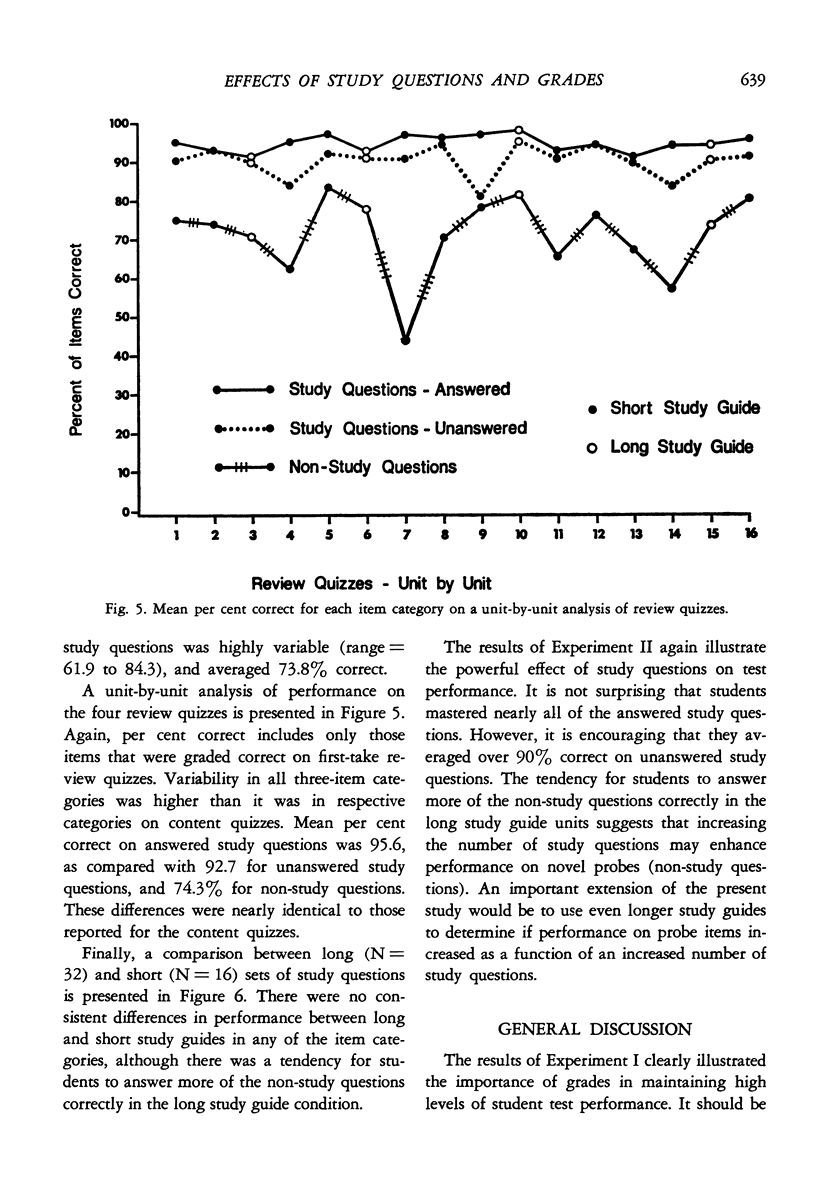
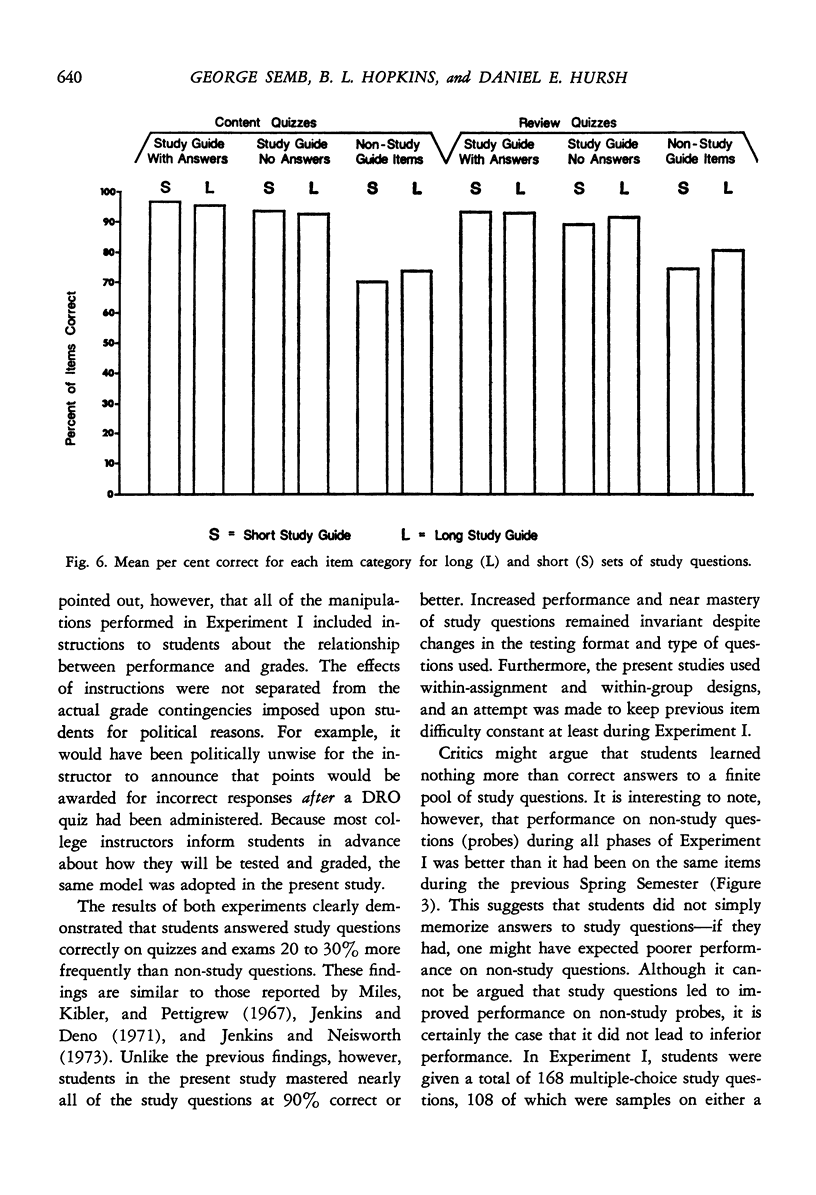
Two experiments demonstrated the effects of study questions on student test performance in an introductory college course. Students in both experiments correctly answered study question items 20 to 30% more frequently than non-study question probes. Furthermore, mean performance on study question items was better than 90% during all phases of both experiments. The present experiments were also designed to study the effects of grades on test performance, and the relationship between long and short sets of study questions. The results of Experiment I clearly illustrated the importance of using grades to maintain high levels of student test performance. The results of Experiment II suggested that long sets of study questions may produce better performance on probe items than do short sets of study questions, but the effect was small.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Born D. G., Gledhill S. M., Davis M. L. Examination performance in lecture-discussion and personalized instruction courses. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):33–43. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F. S. "Good-bye, teacher...". J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):79–89. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael J. S., Corey J. R. Contingency management in an introductory psychology course produces better learning. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):79–83. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard W. C., Macdermot H. G. Design and evaluation of a programmed course in introductory psychology. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Spring;3(1):5–11. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


