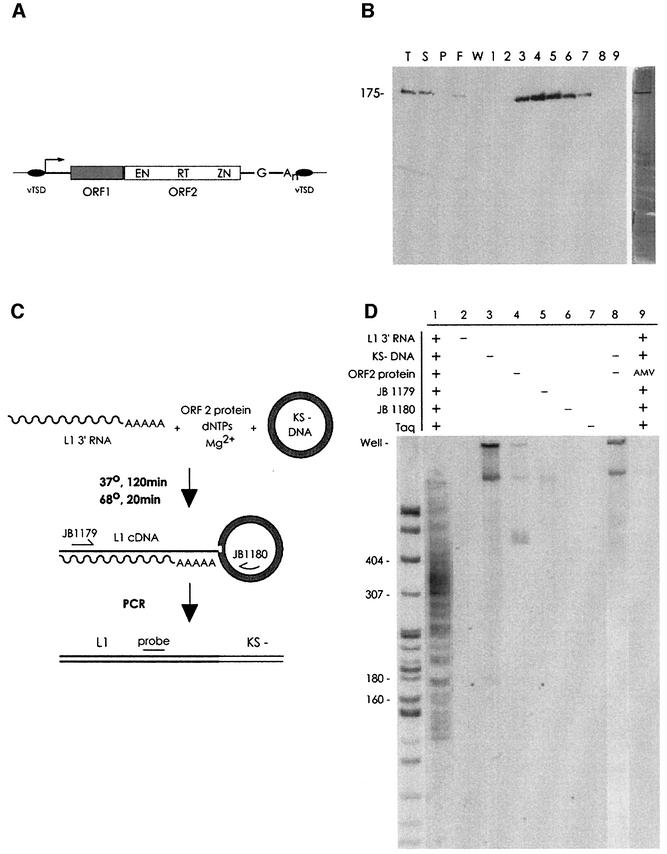
Fig. 1. (A) The human L1 retrotransposon. EN, endonuclease domain; RT, reverse transcriptase domain; ZN cysteine-rich domain; vTSD, variable target site duplication. The 5′ UTR contains an internal promoter (arrow); the 3′ UTR, a polyG and polyA sequence. (B) Protein purification. L1 ORF2p purification was analyzed by electrophoresis and western blotting and silver staining (right panel). T, total lysate; S, supernatant; P, pellet; F, column flow-through; W, wash; 1–9, 0.5 ml GSH elution fractions. (C) Reaction and detection scheme. Incubation of the reaction components results in formation of branched TPRT products. Branched molecules are detected by PCR with primers JB1179 and 1180, followed by Southern blotting with the JB2296 probe. (D) TPRT by L1 ORF2p. Lane 1, full reaction; lanes 2–7, full reaction less the indicated omission; lane 8, to ensure that the products observed in lane 1 were not the result of PCR-mediated target DNA–cDNA recombination, reactions 3 (containing cDNA but no target DNA) and 4 (containing target DNA but no cDNA) were mixed before PCR; lane 9, a full reaction, but with a large excess of AMV RT substituted for L1 ORF2p. The sizing standard used here and throughout is a MspI digest of pBR322, consisting of fragments of the following number of base pairs: 622, 527, 404, 307, 242, 238, 217, 201, 190, 180, 160, 147 and smaller fragments.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.