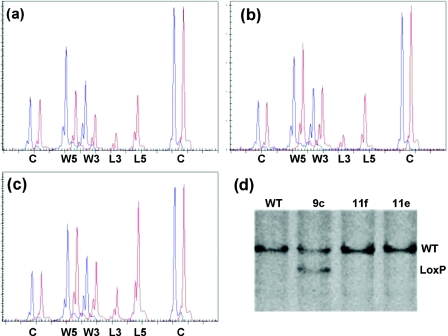
Figure 3.
Identification of homologous and non-homologous recombination for the conditional inactivation of PCNA with MLPA. DNA extracted from targeted and untargeted ES cell clones was analysed by MLPA using a probe mix containing 12 copy number control probes (C) and two MLPA probes specific for both the 5′ and 3′ wild-type (W5 and W3) and LoxP recombination sites (L5 and L3). Only part of the capillary electrophoresis (CE) pattern is shown. (a) CE pattern obtained from untargeted ES cell DNA (blue, WT) and DNA from a homologous recombined ES cell clone (red, 9c). A 50% reduction in both the 5′ (114 bp) and the 3′ (120 bp) wild-type specific signals and the appearance of both 3′ (127 bp) LoxP and the 5′ (134 bp) LoxP specific signals can be seen. (b) CE pattern obtained from a non-homologous recombination. No change is observed in the wild-type specific signals but mutant specific signals appear in the targeted ES cell clone (red, 11f) compared with the control DNA. (c) Two non-homologous integrations can be identified by the 100% increase in the mutant signals compared with the average single integration (red, 11e). (d) Verification of the MLPA results with Southern blot analysis on BamHI digested genomic DNA using an external 3′ probe. Wild-type allele: 11 kb, Conditional allele: 9 kb. (WT) Untargeted ES cells. (9c) Homologous integration. (11e+f) Non-homologous integrations.