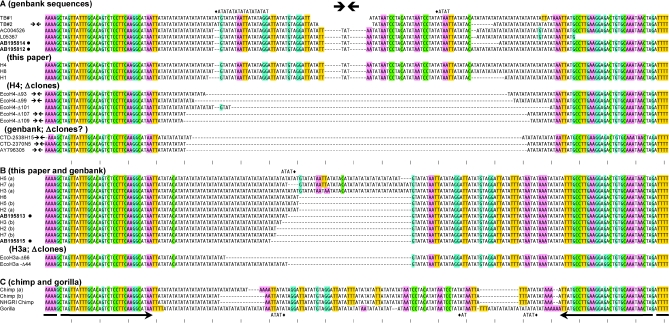
Figure 6.
(A–C) Sequence comparisons of the NF1 site. All human sequences, as well as deletion derivatives fall into two groups, distinguished e.g. by the presence of ‘T’ or ‘C’ 46 bp from the left and TTAT or ATTT 34–37 bp from the right border of the sequence alignment. Chimp and gorilla sequences are given in (C). Where applicable, lower case ‘a’ and ‘b’ differentiate alleles. H7b and H2b were from a parent/child pair. H4 and H6 were from siblings. Other identical alleles such as H3a, H6 and H5b were from unrelated individuals. Known deletion artifacts generated in the TOP10 or TOP10F′ strain of E.coli are designated EcoH4-(#) and EcoH3-(#) in (A) or (B), respectively. All available versions of the 17q11 region in GenBank are given and identified by accession number. Some of these sequences match known deletion artifacts. ‘Chimp NHGRI’ is from the public chimpanzee genome database (see Materials and Methods), and originates from a different animal than the ‘chimp b’ allele sequenced here. Bulleted sequences (accession nos AB195814, AB195812, AB195813 and AB195815) were deposited while this manuscript was in preparation. TB#1 and TB#2 show the chr17 components of derivative 17:22 translocated chromosomes from (18) and (19), respectively. The gap (without dashes) indicates uncertainty because the chromosome 17 or 22 assignments close to the breakpoints of the derivative chromosomes is ambiguous. All sequences were first aligned using Clustal and then hand-adjusted. Presentation of the alignment was simplified by showing excess AT repeats for some sequences on the line above (TB#1, H5a) or below (Gorilla). The AT tract to which these belong is indicated by the diamond. G, C, AAA or TTT sequences are colored (G and C complementarity is indicated by blue and green; A and T are likewise red and yellow respectively). Perfectly palindromic sequences are marked by a double arrow in the left margin.