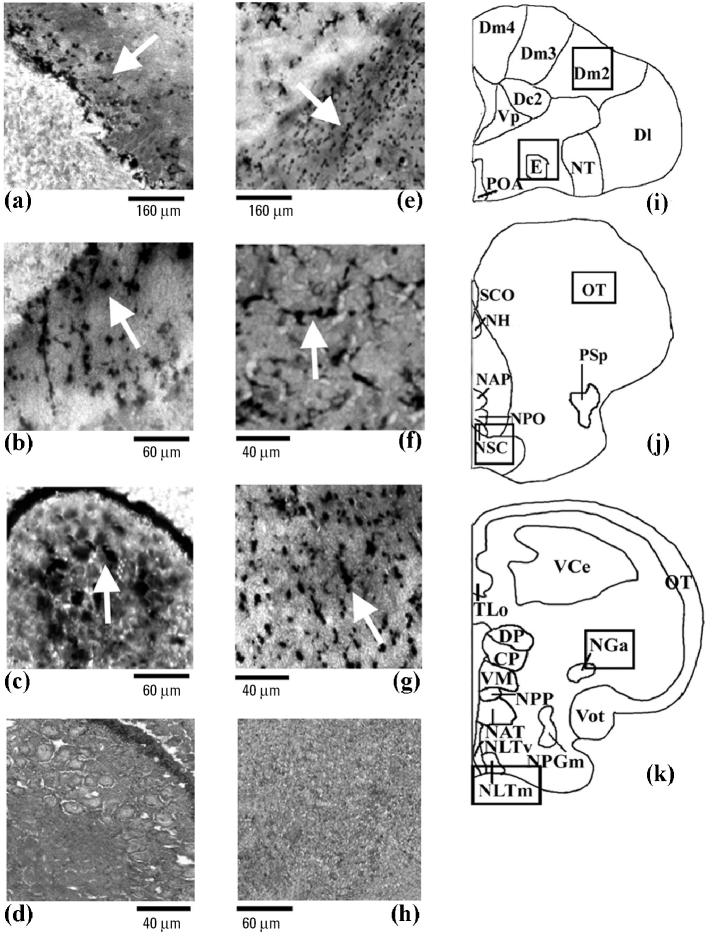
Figure 2.
Photomicrographs showing the amino cupric silver staining pattern in rostral (i), middle (j), and posterior (k) brain areas of the Thalassoma pavo, treated with a MAT concentration of (a–c) Cd or (e–g) endosulfan. The effects of Cd (n = 6; arrows) were mostly observed in telencephalic and in mesencephalic areas such as Dm2 (a) and in the piriform SGC neurons of the optic tectum (b), respectively, and in the pretectal NGa (c), compared with control (n = 8); controls gave comparable results at all brain levels for both neurotoxicants as described in “Materials and Methods,” and so these same controls (d, h) were also used for the effects of endosulfan. In the case of endosulfan (n = 6), the major effects (arrows) were detected in the interneurons of the entopeduncular nucleus (e) and in the preoptic NSC area (f) and NLTm (g) of the hypothalamic lobe.
Abbreviations: CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; Dc2, central part of dorsal telencephalon, subdivision 2; Dl, lateral part of the dorsal telencephalon; Dm2–Dm4, medial part of the dorsal telencephalon, subdivisions 2–4; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; E, entopeduncular nucleus; NAP, anterior periventricular nucleus; NAT, anterior tuberal nucleus; NGa, anterior part of the nucleus glomerulosus; NH, habenular nucleus; NLTm, medial part of lateral tuberal nucleus; NLTv, ventral part of lateral tuberal nucleus; NPGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; NPO, preoptic nucleus; NPP, posterior periventricular nucleus; NSC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; NT, nucleus taenia; OT, optic tectum; POA, preoptic area; PSp, parvocellular superficial pretectal nucleus; SCO, subcommissural organ; TLo, torus longitudinalis; VCe, cerebellum valvula; VM, ventromedial thalamic nucleus; Vot, ventral optic tract; Vp, postcommissural nucleus of the ventral telencephalon.