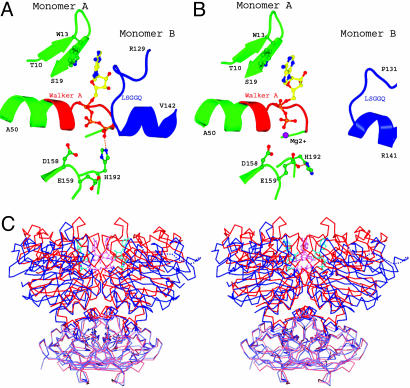
Fig. 4.
Conformational changes of MalK upon ATP hydrolysis. (A and B) The nucleotide-binding site of the ATP-bound dimer structure, with ATP sandwiched between the Walker A and B motifs of one monomer and the LSGGQ motif of the other monomer (A) and the posthydrolysis ADP-bound structure (B). The color scheme is similar to that of Fig. 2. (C) Stereoview of superimposed MalK structures in the ATP-bound (red) and ADP-bound (blue) forms. The RDs are rendered in lighter color than the NBDs. ATP (pink) and ADP (cyan) molecules are shown in ball-and-stick model.