Fig. 5.
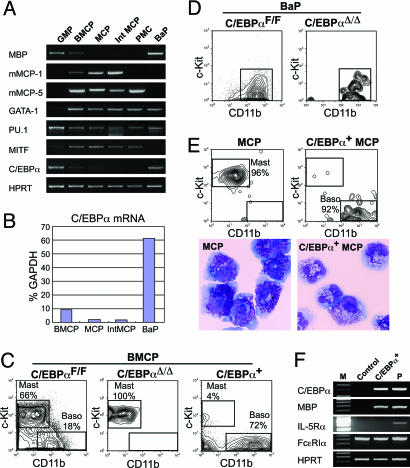
C/EBPα plays a key role in the bifurcation of mast cell vs. basophil lineage fates. (A) RT-PCR analyses of lineage-related gene expression in purified progenitor populations. GMPs and BaPs were purified from the bone marrow, and BMCPs were from the spleen of C57BL/6 mice. MCP, GMP-derived MCPs after in vitro culture (see text and Fig. 3B); Int MCP, intestinal MCPs; PMC, peritoneal mast cells. (B) A quantitative real-time PCR assay for C/EBPα mRNA in purified populations. (C) FACS analyses of progeny of spleen BMCPs with or without C/EBPα. BMCPs isolated from the spleen of C/EBPαF/F mice were infected with retroviruses carrying control GFP (Left), Cre recombinase (Center), or C/EBPα (Right). GFP+ cells were phenotyped after 7 days in culture. (D) FACS analyses of progeny of bone marrow BaPs disrupted with C/EBPα. BaPs differentiated only into c-Kit-CD11b+ basophils in vitro, irrespective of C/EBPα disruption. (E) Analysis of intestinal MCPs transduced with C/EBPα. MCPs infected with control retroviruses differentiated exclusively into CD11b-c-Kit+ mature mast cells, whereas those transduced with C/EBPα converted into CD11b+c-Kit- basophils. The morphology of progeny of GMP-derived MCPs transduced with control retroviruses (Lower Left) and with C/EBPα (Lower Right) is also shown. May-Giemsa staining was used. (Magnification: ×1,000.) (F) RT-PCR analyses of basophil-related genes in progeny of MCPs with or without ectopic expression of C/EBPα. P, positive control.