Figure 4. Outer hair cell electromotility.
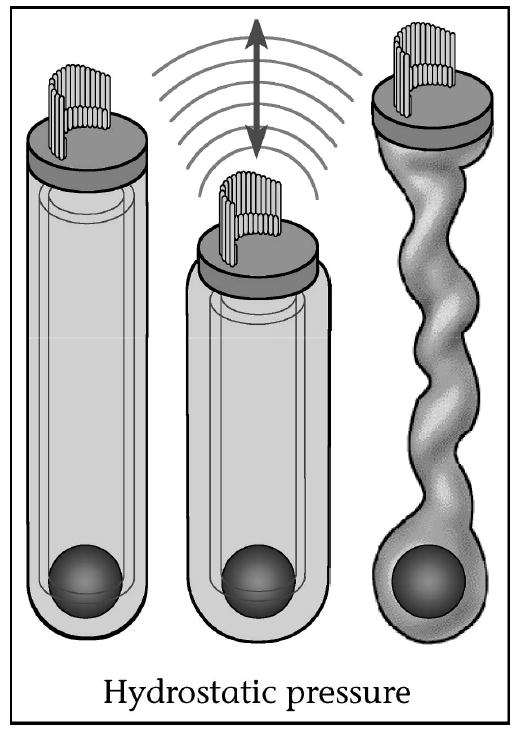
Outer hair cell electromotility. Outer hair cells contract and elongate with each cycle of sound as their intracellular voltage changes. This amplifies the vibration of the organ of Corti, permitting exquisite hearing sensitivity and frequency selectivity. OHCs have an intracellular turgor pressure to help maintain their shape. Loss of OHC turgor pressure causes the cell to constrict so that it can no longer produce electromotile force. Figure derived from Brownell (1999) [85].
