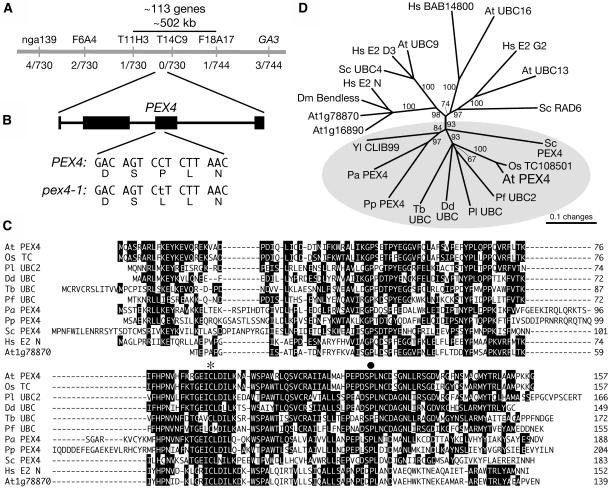
Figure 1.
pex4-1 Is Defective in a UBC Enzyme.
(A) Recombination mapping was used to localize pex4-1 to the middle of chromosome 5, represented by the gray bar. IBA-resistant plants were scored using PCR-based markers (above the bar), and the number of recombination events/total number of chromosomes are shown below the bar.
(B) Sequence analysis of a candidate gene using mutant DNA revealed a C-to-T mutation in the third exon (black rectangle) of PEX4, altering a conserved Pro to a Leu in the encoded protein.
(C) Sequence alignment of Arabidopsis (At) PEX4 with its closest Arabidopsis homolog (At1g78870) and similar proteins from the monocot plant rice (Oryza sativa; Os); the algae Pavlova lutheri (Pl); the protists Dictyostelium discoideum (Dd), Trypanosoma brucei (Tb), and Plasmodium falciparum (Pf); the yeast Pichia angusta (Pa), P. pastoris (Pp), and S. cerevisiae (Sc); and the metazoan Homo sapiens (Hs). Sequences were aligned with the MEGALIGN program (DNASTAR) using the ClustalW method with Gonnet series protein weight matrix. Residues identical in a majority of sequences are indicated by black boxes. The active site Cys is marked with an asterisk, and the pex4-1 mutation is indicated by a circle.
(D) Phylogenetic tree of PEX4 relatives from (C) with additional UBC proteins, including representatives from Drosophila melanogaster (Dm) and Yarrowia lipolytica (Yl). The unrooted phylogram was generated with PAUP 4.0b5 (Swofford, 2001) using the alignment shown in Supplemental Figure 1 online. The bootstrap method was performed for 100 replicates with a distance optimality criterion, and all characters were weighted equally. Bootstrap values are at the tree nodes, and characterized and predicted PEX4 proteins are highlighted in the gray oval.