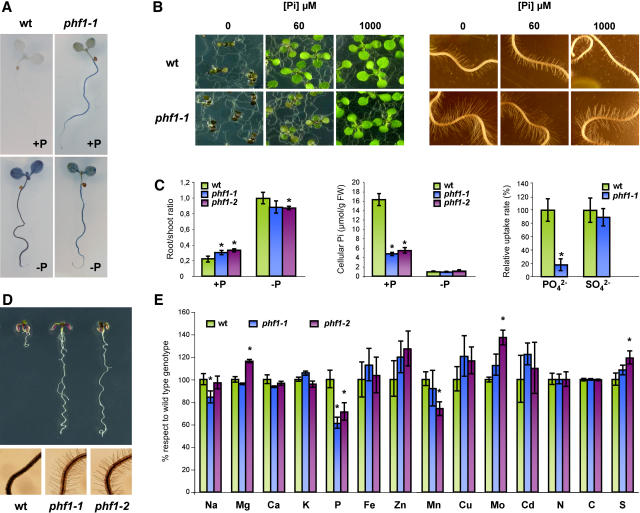
Figure 1.
Phenotypic Characteristics Associated with the phf1 Mutant Alleles.
(A) Histochemical analysis of GUS activity driven by the IPS1:GUS reporter gene in wild-type and phf1-1 plants grown in Pi-rich (+P) or Pi-deficient (−P) medium.
(B) Wild-type and phf1-1 plants after growth on medium containing 0, 60, or 1000 μM Pi (left). Details of their root hairs are shown at right.
(C) Histograms of root/shoot growth ratio, cellular Pi content, and Pi and SO42− uptake for the wild type and phf1 mutants. FW, fresh weight.
(D) Wild-type, phf1-1, and phf1-2 plants after growth in Pi-deficient medium supplemented with 10 ppm arsenate.
(E) Histogram showing the relative contents of different elements in the wild type and phf1 mutant alleles after growth in complete medium.
In all instances, plants were grown for 12 d, except for the histochemical staining (A), root hair growth (B), and Pi and SO42− uptake (C) experiments, in which plants were grown for 5, 5, and 8 d, respectively. Standard deviations are indicated by error bars. Statistically significant differences between the wild type and either allele (P < 0.05, according to Student's t test) are marked with asterisks.