Figure 3.
Morphology of Δgas1 Mutant Strains.
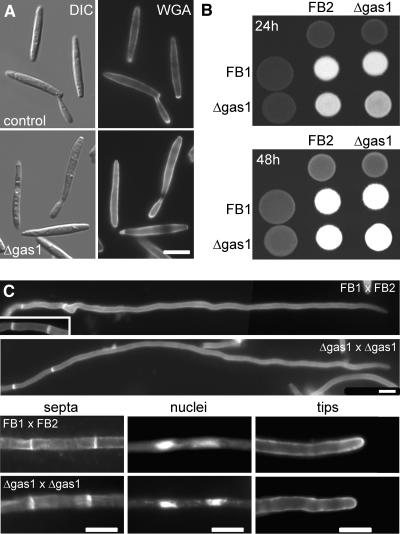
(A) Haploid sporidia of wild-type strain FB2 (top panel) and Δgas1 strain HUB14 (bottom panel) as visualized by differential interference contrast optics (left panel) and after staining for chitin with fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated WGA (right panel). The lateral walls of Δgas1 mutant cells are more strongly stained, suggesting that chitin is more accessible to the dye. Bar = 5 μm.
(B) Mating assays of wild-type and mutant strains. Wild-type (FB1 and FB2) and Δgas1 mutant strains (HBU13 and HBU14) were spotted on charcoal-containing agar plates either as pure cultures or as mixtures with the compatible strains and incubated for 24 h (top panel) or 48 h (bottom panel) at 20°C. The appearance of white filaments indicates formation of dikaryotic hyphae. The cross of Δgas1 mutant strains develops dikaryotic hyphae slightly slower.
(C) Dikaryotic hyphae formed by a cross of the wild-type strains FB1 and FB2 or the Δgas1 mutant strains HBU13 and HBU14 after 24 h on charcoal-containing agar plates. Both wild-type and Δgas1 hyphae are straight, grow with a long extended tip cell, and form basal empty sections (top panel). With both strain combinations, these sections are limited by two septa as visualized using WGA (septa, bottom left panel). The tip cells of both strain combinations contain two nuclei as seen by 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) straining of DNA (nuclei, lower middle panel) and carry a cap of chitin at the tip (tips, bottom right panel), indicating growth by tip extension. Bars = 10 μm.