Figure 1.
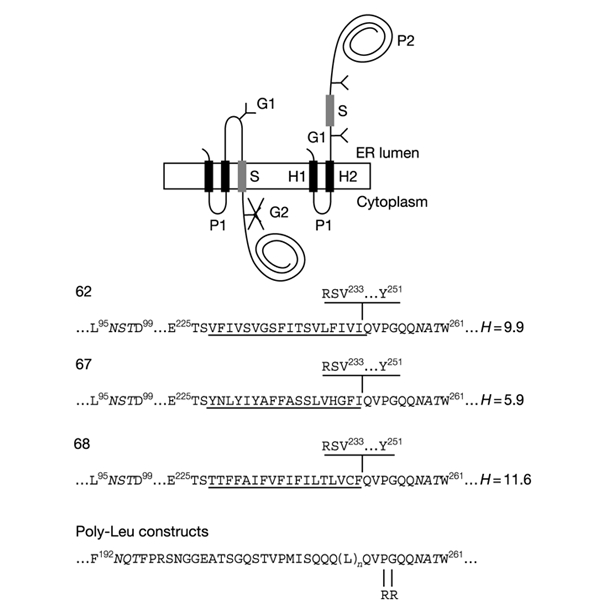
Model proteins. Lep has two transmembrane segments (H1, H2) and a large globular domain (P2). Different S-segments were inserted into the P2 domain in the location shown. Y indicates Asn-X-Thr glycosylation acceptor sites (G1, G2). Expressed proteins with a single glycosylated site (G1) have an S-segment with stop-transfer activity (top left), while those with two modified sites (G1, G2) have an S-segment that does not integrate into the membrane (top right). The amino-acid sequences of the relevant regions around the S-segments of the different constructs are shown at the bottom. Numbered residues indicate positions in the Lep wild-type protein. The G1 and G2 glycosylation sites are shown in italics. S-segments are underlined. The sequence RSV...Y shown above the sequences for clones 62, 67, and 68 is present only in the longest constructs tested (carboxy tail length = 92 residues). Carboxy tail lengths are counted from the first residue immediately downstream of the underlined S-segments (Gln in the case of all constructs except for those with a carboxy tail length of 92 residues, where counting starts from Arg). The mean hydrophobicities (H, calculated as described in Methods) of the S-segments in clones 62, 67, and 68 are also given. The Arg-Arg mutation in the poly-Leu constructs is shown.
