Figure 2.
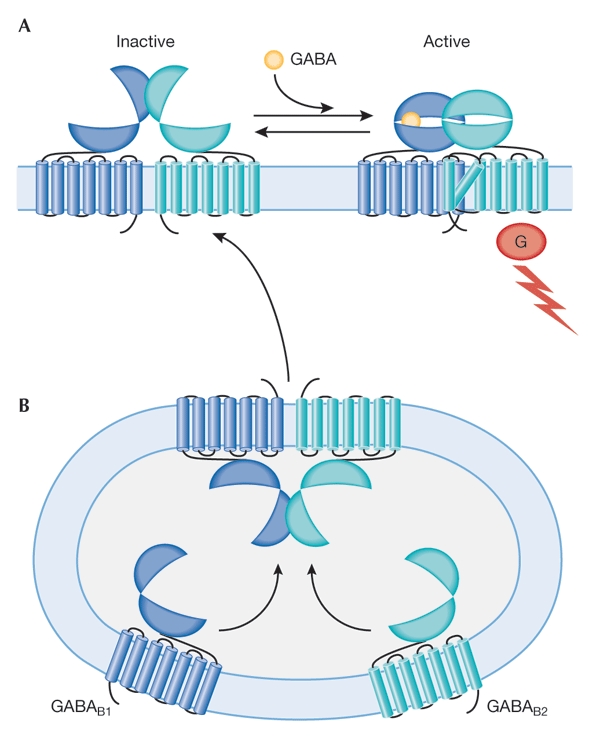
Functional expression of γ-aminobutyric acid B receptors. GABAB receptors are responsible for presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmitter release in the mammalian brain, and function as heterodimers that consist of GABAB1 and GABAB2 subunits. (A) Whereas the GABAB1 receptor is essential for responses elicited by the binding of GABA, the GABAB2 receptor mediates G-protein activation (Galvez et al., 2001). (B) GABAB1- and GABAB2-receptor subunits probably assemble in transport vesicles. Trafficking of the heterodimer to the cell surface depends on the presence of the GABAB2 receptor. G, G protein.
