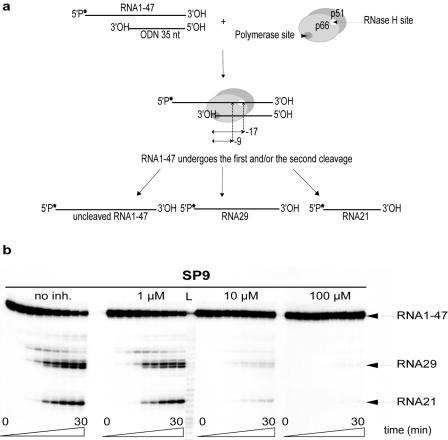
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of RNase H activity by 3,7-dihydroxytropolones. (a) Experimental design and expected products of polymerase-dependent RNase H activity. In this mode of cleavage, the polymerase active site is positioned at the 3′ end of the DNA primer (ODN35) and determines the position of the cleavage 17 nt downstream, yielding RNA29. RT is also able to cut 9 nt from the 3′ end of the DNA strand, producing RNA21. The 32P-labeled 5′ end of RNA1-47 is indicated by an asterisk. (b) Inhibition of RNase H activity by SP9. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 10 nM HIV-1 RT to 10 nM of RNA1-47/ODN35 complex, in the absence (no inhibitor [inh.]) or presence of 1 μM, 10 μM, or 100 μM of SP9. The reaction was stopped after 0, 15, or 30 s or 1, 3, 5, 10, 20, or 30 min. Lane L corresponds to a RNA ladder that was used to determine the sizes of the products.