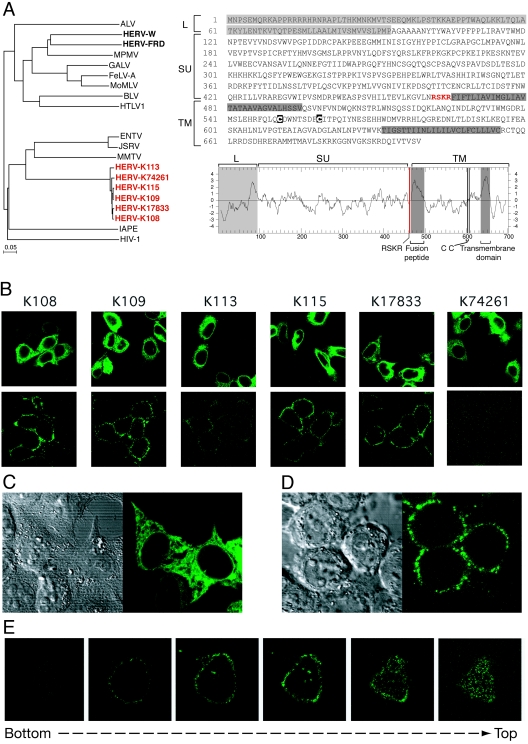
FIG. 1.
Structure and expression of the HERV-K ENV proteins. (A, left) Phylogenetic tree based on the ENV TM domain showing the clustering of the six HERV-K copies with the betaretrovirus group. Protein sequences were aligned using ClustalW, and the resulting alignment was manually refined before the tree was calculated using the neighbor-joining method (PHYLIP software). Nucleotide sequences of the six env genes are as follows (accession number, position in the sequence entry, orientation): for K108, AC072054, 30,365 to 32,464 (minus); for K109, AF164615, 6,412 to 8,508 (plus); for K113, AY037928, 6,451 to 8,550 (plus); for K115, AY037929, 6,442 to 8,541 (plus); for K17833, Y17833, 5,581 to 7,680 (plus); and for K74261, AC074261, 93,508 to 95,604 (plus). (Right) Sequence and hydrophobicity profile of the HERV-K108 ENV highlighting the canonical ENV features (see the text). ALV, avian leukemia virus; MPMV, Mason-Pfizer monkey virus; GALV, gibbon ape leukemia virus; FeLV-A, feline leukemia virus A; MoMLV, Moloney MLV; BLV, bovine leukemia virus; HTLV1, human T-cell leukemia virus type 1; ENTV, enzootic nasal tumor virus; JSRV, Jaagsiekte sheep retrovirus; MMTV, mouse mammary tumor virus; IAPE, intracisternal A-particle-related envelope-encoding element. (B-E) Immunofluorescence analysis of HeLa cells transiently transfected with expression vectors of each of the six fully coding HERV-K env genes. (B) In the upper panels, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for HERV-K env expression (whole-cell staining); in the lower panels, living cells were observed directly after staining without prior fixation or permeabilization (cell surface staining). (C, D) Higher magnification of representative images of fixed and permeabilized cells (C) or of living cells (D) transfected previously with the HERV-K108 env gene. (Left) Image of the cells under phase-contrast microscopy; (right) image of the same cells stained for the HERV-K ENV by immunofluorescence. (E) Successive confocal images of a living cell stained for the HERV-K108 ENV, demonstrating cell surface localization. In all experiments, HERV-K ENV detection was performed on HeLa cells grown on glass coverslips approximately 24 h posttransfection. HERV-K ENVs were detected using a mouse monoclonal antibody (raised by us against a recombinant His-tagged protein corresponding to amino acids 223 to 437 of K109 ENV, using the pET-28 vector from Novagen), and an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody (Molecular Probes). No signal was detected with cells transfected with an irrelevant expression vector (not shown). Observations were made under a Zeiss LSM 510 laser scanning confocal microscope.