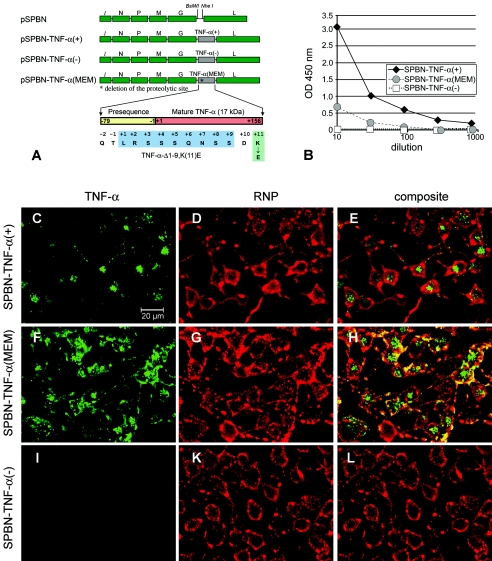
FIG. 1.
Expression of TNF-α by recombinant RV. (A) Schematic of RV-TNF-α recombinant constructs. The pSPBN vector was derived from SN by removing the Ψ gene and introducing BsiWI and NheI sites between the G and L genes. Mouse TNF-α cDNA was amplified by PCR, with the introduction of BsiWI and NheI sites, and was ligated into pSPBN, resulting in pSPBN-TNF-α(+). In pSPBN-TNF-α(MEM), the proteolytic cleavage site of TNF-α was removed by deleting the coding sequence for the first nine amino acids of soluble TNF-α and exchanging the lysine at position 11 with glutamic acid, as described in Materials and Methods. To construct pSPBN-TNF-α(−), the first seven ATG codons of the TNF-α gene were mutated. (B) TNF-α production in BSR cells. BSR cells were infected with SPBN-TNF-α(−), SPBN-TNF-α(MEM), or SPBN-TNF-α(+) at an MOI of 0.1 and incubated at 37°C. TNF-α secreted into the tissue culture supernatants of infected BSR cells was measured at 24 h p.i., using ELISA. OD, optical density. (C to L) Confocal double-immunofluorescence microscopy of TNF-α (green, panels C, F, and I) and rabies ribonucleocapsid (RNP) (red, panels D, G, and K) in NA cells infected with SPBN-TNF-α(+), SPBN-TNF-α(MEM), or SPBN-TNF-α(−). Panels E, H, and L show the composites of TNF-α and RNP double immunofluorescence. Note that TNF-α is absent only in NA cells infected with SPBN-TNF-α(−) (panels I and L).