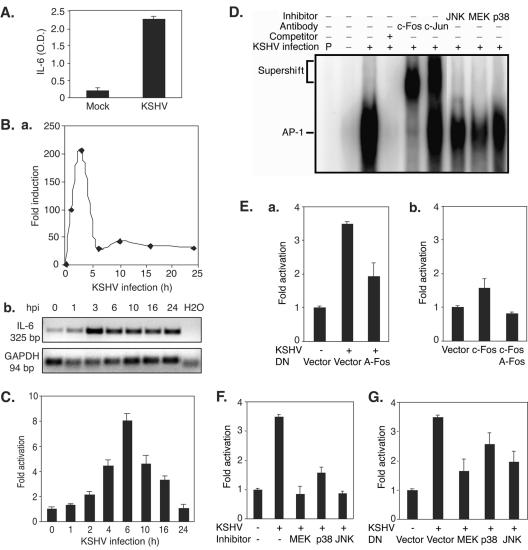
FIG. 7.
KSHV induces IL-6 expression through AP-1 activation and is mediated by multiple MAPK pathways. (A) KSHV infection induces IL-6 secretion into the culture medium. The culture medium from mock- or KSHV-infected HUVEC was collected at 6 hpi and assayed for IL-6 by ELISA. (B) KSHV infection induces expression of the IL-6 transcript. Total RNA isolated from HUVEC infected with KSHV for different time points was assayed for the abundance of IL-6 transcripts by RT-qPCR. The relative abundances of IL-6 transcripts were calculated by setting mock-infected cells (0 h) as onefold (a). Transcripts of human GAPDH were used to calibrate loading. Products from RT-qPCR were also examined on a gel to confirm the results (b). (C) KSHV infection activated the IL-6 promoter reporter. Cells (293 cells) were transfected with IL-6 reporter plasmid DNA and assayed for luciferase activity at 36 h posttransfection. Prior to harvest, the cells were infected with KSHV for 0, 2, 4, 6, 10, and 16 h. (D) KSHV infection induces binding of AP-1 complexes to the consensus element in the IL-6 promoter. Cells (293 cells) were infected with KSHV for 6 h. The experimental conditions are described in the legend to Fig. 2. (E) DN c-Fos (A-Fos) inhibited induction of the IL-6 promoter by KSHV infection. Cells (293 cells) cotransfected with IL-6 reporter plasmid DNA together with A-Fos or a vector control for 30 h were either mock infected or infected with KSHV for 6 h, lysed, and assayed for luciferase activity (a). As controls, the IL-6 reporter was cotransfected with a vector control or an active form of c-Fos, with or without A-Fos (b). (F) Inhibitors of MAPK pathways prevent activation of the IL-6 reporter during KSHV primary infection. Cells (293 cells) transfected with IL-6 reporter plasmid DNA for 30 h were either mock infected or infected with KSHV for 6 h, with or without specific inhibitors of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK, lysed, and assayed for luciferase activity. The inhibitors were added 1 h prior to KSHV infection. (G) Inhibition of MAPK pathways with DN constructs reduces activation of the IL-6 reporter during primary KSHV infection. Cells (293 cells) transfected with IL-6 reporter plasmid DNA alone or together with DN constructs of MEK, p38, and JNK for 30 h were either mock infected or infected with KSHV for 6 h, lysed, and assayed for luciferase activity. All KSHV infection experiments were carried out at an MOI of 2. For the IL-6 ELISA (A), the experiments were independently carried out two times, with three repeats each. The results are averages with standard deviations from one representative experiment. For IL-6 RT-qPCR (B), the experiments were independently carried out two times, with three repeats each. The results are from one set of samples from one representative experiment. For the reporter assay (C, E, F, and G), the experiments were independently carried out three times, with three repeats each. The results presented are averages with standard deviations from one representative experiment. For EMSA (D), the experiments were repeated two times. The results presented are from one representative experiment.