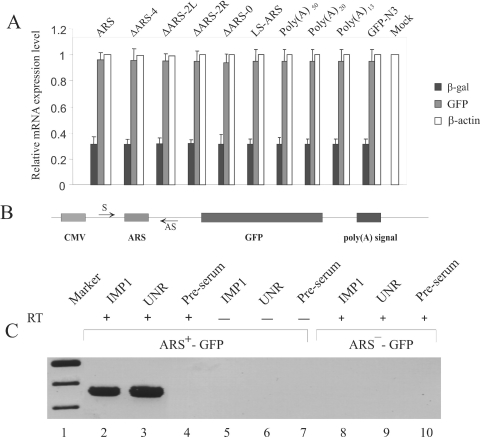
Figure 7.
Analysis of the reporter mRNA. (A) Measurement of mRNA levels by real-time RT–PCR. HeLa cells were transfected with various GFP reporter constructs to express GFP mRNA containing either poly(A) of different length, wild-type or mutant ARS elements in their 5′-UTR. Cells were co-transfected with pCMV-SPORT-β-gal vector as a control for the transfection efficiency between experiments. Total cellular RNA from the transfected cells was analyzed by real-time RT–PCR using gene specific primers (Table 3) as described in Materials and Methods. Two separate analyses for each of the four independent transfection experiments were performed and averages of eight measurements are presented here. The β-actin mRNA level was measured as an internal loading control. PCR of RNA from the ARS-pEGFP-N3 transfected cells was carried out without performing the reverse transcription step as a negative control. (B) In vivo RNA–protein crosslinking and immunoprecipitation. In vivo crosslinked RNPs were immunoprecipitated using IMP1 and UNR antibodies. The presence of GFP reporter mRNA in the immunoprecipitae was analyzed by RT–PCR. Samples without the reverse transcription step (RT-) were also used in PCRs to monitor the absence of any contaminating plasmid DNA. Lane 1, DNA marker; lanes 2–4, RT–PCR analysis of ARS+-GFP samples immunoprecipitated using IMP1, UNR, and rabbit pre-serum, respectively. Lanes 5–7, analysis of ARS+-GFP samples immunoprecipitated using IMP1, UNR and rabbit pre-serum without RT reaction, respectively. Lanes 8–10, RT–PCR analysis of ARS−-GFP samples immunoprecipitated using IMP1, UNR and rabbit pre-serum, respectively.