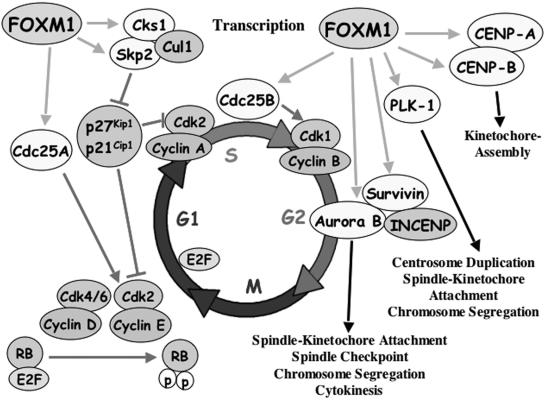
FIG. 10.
Model summarizing Foxm1 target genes involved in regulating G1/S and G2/M progression. FoxM1 protein is necessary for expression of Cdc25A phosphatase, which is required to dephosphorylate and stimulate Cdk2 kinase activity (52). Foxm1 regulates transcription of the Skp2 and Cks1 genes, which are specificity subunits essential for recognition of phosphorylated CDKI proteins p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 by the Skp1-Cullin1-F-box (SCF) ubiquitin ligase complex to target these CDKI proteins for ubiquitin-mediated proteasome degradation (11, 19, 49, 59, 63). Diminished nuclear levels of CDKI proteins p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 are required for stimulating Cdk2-cyclin E complex activity that cooperates with Cdk4/6-cyclin D to phosphorylate the RB protein and activates E2F to stimulate transcription of S-phase genes (45). For progression into mitosis, Foxm1 transcriptionally activates Cdc25B phosphatase (67), which is required to dephosphorylate and activate Cdk1 kinase (52). FoxM1 regulates transcription of PLK1 (37) or Aurora B kinase and survivin, which forms a complex with INCENP and regulates numerous stages of mitosis (48). FoxM1 regulates transcription of CENPA and CENPB, both of which are essential for kinetochore assembly.