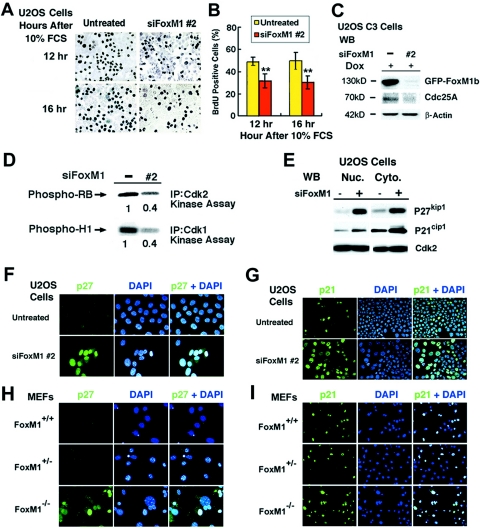
FIG. 8.
FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells and Foxm1−/− MEFs exhibit increased nuclear levels of CDKI proteins. (A) Diminished BrdU incorporation rates in serum-stimulated FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells. FoxM1-depleted or untreated U2OS cells were serum starved for 48 h and then stimulated to reenter the cell cycle with the addition of 10% fetal calf serum and cells at 12 and 16 h after serum stimulation and a 1-hour pulse-label with BrdU before harvesting the cells. (B) Graph quantitating BrdU incorporation rates in serum-stimulated FoxM1-depleted and control U2OS cells. We counted the number of BrdU-positive cells from three distinct 200× fields at 12 and 16 h after serum stimulation (in triplicate), and this was used to calculate the percentage of cells with BrdU incorporation ± the SD as shown graphically. Statistically significant decreases in the percentage of BrdU incorporation were found in serum-stimulated FoxM1-depleted U2OS as determined by the Student t test (**, P < 0.01). (C) FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells displayed reduced levels of Cdc25A phosphatase protein as determined by Western blot analysis. (D) FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells exhibited diminished Cdk1 and Cdk2 kinase activities. FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells were IP with Cdk2 or Cdk1 antibodies and used for radioactive kinase assays with either recombinant Cdk2 substrate RB protein or Cdk1 substrate histone H1 protein. The radioactively labeled phosphorylated substrates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by autoradiography and then quantitated by the Kodak BioMax 1D program. (E) FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells exhibited increased nuclear and cytoplasmic levels of the CDKI proteins p27Kip1 and p21Cip1 as determined by Western blot analysis. FoxM1-depleted or untreated U2OS cells were used to prepare nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts for Western blot analysis with antibodies specific to either the p27Kip1 or p21Cip1 proteins. Both FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells (F) and early-passage Foxm1−/− MEFs (H) exhibited increased nuclear staining of the CDKI protein p27Kip1 compared to low levels in untransfected U2OS cells and WT or Foxm1+/− control MEFs. The number of nuclei expressing high levels of the CDKI protein p21Cip1 was significantly increased in FoxM1-depleted U2OS cells (G) and early-passage Foxm1−/− MEFs (I) compared to untransfected U2OS cells and WT or Foxm1+/− MEF controls. Passage 3 Foxm1+/+ (WT), Foxm1+/−, or Foxm1−/− MEFs and FoxM1-depleted or untreated U2OS cells were immunofluorescently stained with monoclonal antibody specific to either p27Kip1 (400×) or p21Cip1 proteins (200×), nuclei were counterstained with DAPI, and this was merged with CDKI immunofluorescent staining.