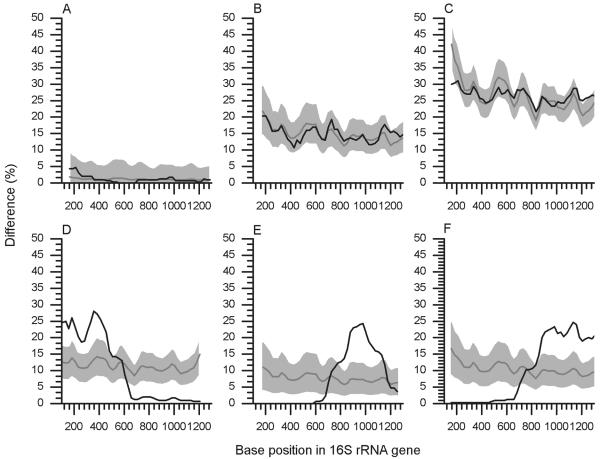
FIG. 2.
Typical 16S rRNA gene sequence comparison plots generated by Pintail (all graphs generated with window size 300 and step size 25). (A to C) Plots between pairs of trusted sequences of increasing evolutionary distance, while D to F show examples where the query sequence is a chimera. Observed percentage differences between sequences are plotted as black lines. Gray lines show the expected percentage differences for the sequence pairs. Light gray shading indicates expected percentage differences ±5%. Escherichia coli ATCC 11775T (X80725) is compared to Escherichia vulneris ATCC 33821T (X80734) (A), Pseudomonas aeruginosa LMG 1242T (Z76651) (B), and Aquifex pyrophilus (T) Kol5a (M83548) (C). (D to F) Three typical chimeric patterns. (D) The three-fragment Nitrospira chimeric sequence AY373422 (estimated breakpoints, 340 and 740) is compared to its BLAST identified nearest neighbor, X82559. (E) The three fragment chimeric record U10877 generated from Riemerella anatipestifer (T) ATCC 11845 is shown to diverge from the sequence of its nearest neighbor, R. anatipestifer strain 115/02 (AY856450) around E. coli positions 790 to 1130. (F) The two-fragment Fusobacteria chimeric sequence AY548989 (estimated breakpoint, 800) is compared to the sequence from its nearest neighbor, AY548984.