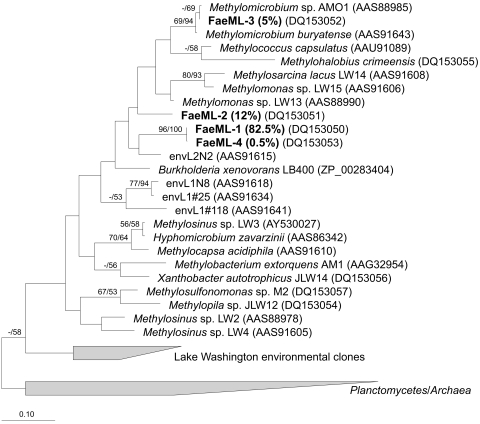
FIG. 1.
Phylogenetic tree reflecting relationships of Fae sequences detected in Mono Lake water column. Analyses were performed using neighbor-joining (NJ) and maximum parsimony (MP) methods, using inferred amino acid sequences (92 positions). The scale bar indicates the number of expected amino acid substitutions per site per unit of branch length. Bootstrap values above 50% for NJ/MP analyses are shown above branches. Note that two types of fae are found in Methylosinus strains (represented here by Methylosinus sp. LW2 and Methylosinus sp. LW3) that cluster separately on phylogenetic trees (12).