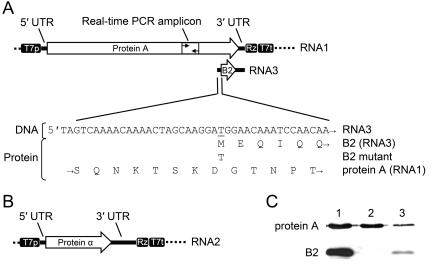
FIG. 3.
Features of the GGNNV transcription vectors used in the current study. (A) Schematic of TVT7R(0,0)-based RNA1 transcription vector pGGNNV1(0,0), showing the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs), protein A and B2 coding regions, and T7 promoter/terminator and self-cleaving ribozyme elements. The T-to-C point mutation in the B2 start codon (ΔB2 mutant) is indicated in the sequence below. (B) Schematic of the RNA2 transcription vector pGGNNV2(0,0), showing the coat protein α coding region, UTRs and vector transcriptional elements. (C) Immunoblot detection of the 110-kDa protein A and 8.5-kDa protein B2 in transfected BSR T7/5 and infected SB cells. Lanes: 1, BSR T7/5 transfected with pGGNNV1(2,0); 2, BSR T7/5 transfected with pGGNNV1ΔB2(2,0); 3, SB infected with GGNNV at a multiplicity of infection of 1. Total cell protein (20 to 30 μg) from transfected or infected cells was prepared at 24 h posttransfection or postinfection, separated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-protein A or anti-B2 antibodies. See Materials and Methods for experimental details.