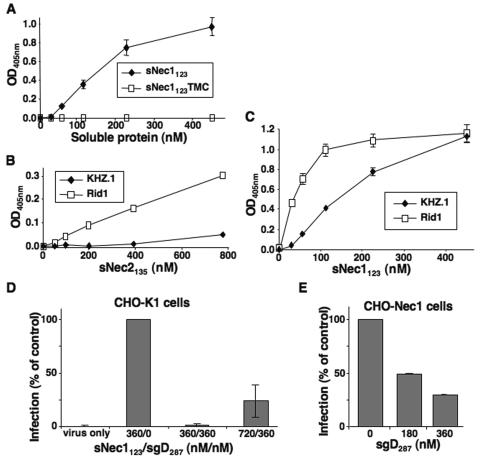
FIG. 3.
Specificity of sNec1123-mediated entry. Results are from ONPG assays 16 h after plating. (A) Comparison of QOZHG entry mediated by sNec1123 and the gD binding-defective mutant derivative sNec1123TMC. CHO-K1 cells were infected at an MOI of 1 in the presence of increasing amounts of sNec1123 or sNec1123TMC protein. (B) Virus entry mediated by soluble nectin-2 V domain (sNec2135). CHO-K1 cells were infected with replication-competent, lacZ-expressing viruses containing wild-type gD (KHZ.1) (60) (MOI = 12) or rid1 mutant gD (KOS-Rid1/tk12) (77) (MOI = 6) in the presence of increasing amounts of sNec2135 protein. (C) Entry of KHZ.1 (MOI = 6) and KOS-Rid1/tk12 (MOI = 3) in the presence of sNec1123. (D) Inhibition of the entry-promoting activity of sNec1123 by preincubation of the soluble receptor with soluble gD ectodomain, sgD287. Soluble receptor and soluble gD were mixed in the indicated molar proportions (nM/nM) and incubated for 15 min at 4°C. QOZHG was then added, and the mixture was incubated for another 15 min at 4°C. CHO-K1 cells in suspension were then infected at 37°C for 50 min (MOI = 3) and plated with fresh medium. The numbers under the bars show the concentrations of the two soluble molecules during infection. Results are expressed as percent infection relative to the positive (360/0) control. (E) Inhibition of infection of receptor-bearing cells by soluble gD. CHO-Nec1 cells in suspension were incubated with sgD287 at the indicated concentrations for 30 min at 4°C prior to infection with QOZHG (MOI = 3) for 50 min at 37°C. Results are expressed as percent infection relative to the control without sgD. All results represent averages of triplicate determinations, and each experiment was performed at least twice.